- NEWS FEATURE
- Correction 17 September 2024
Dozens of labs around the world are striving to grow models of human embryos to study development, fertility and therapies. They are entering uncharted ethical territory.
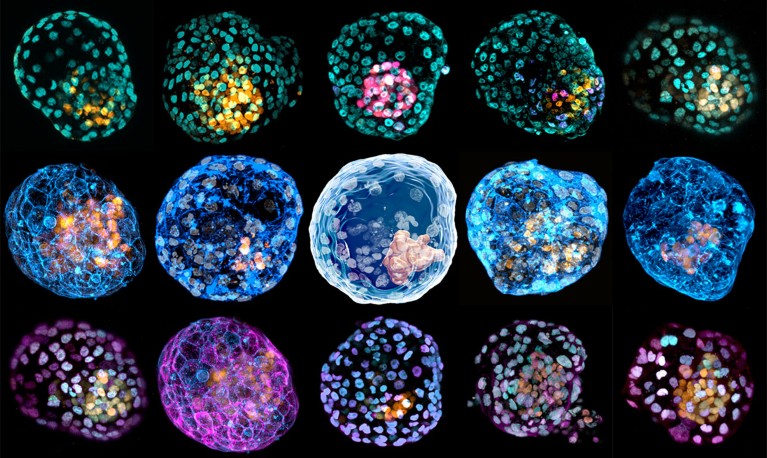
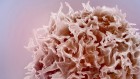
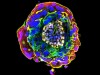
Models of human embryos at the blastocyst stage, which are called blastoids. Credit: Monash Univ.
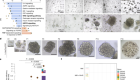
Under his microscope, Jun Wu could see several tiny spheres, each less than 1 millimetre wide. They looked just like human embryos: a dark cluster of cells surrounded by a cavity, and then another ring of cells.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 633, 268-271 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-02915-3
Updates & Corrections
-
Correction 17 September 2024: An earlier version of the animated image erroneously stated that the model represented a 16-cell embryo.
References
Warmflash, A., Sorre, B., Etoc, F., Siggia, E. D. & Brivanlou, A. H. Nature Methods 11, 847–854 (2014).
Moris, N. et al. Nature 582, 410–415 (2020).
Yu, L. et al. Nature 591, 620–626 (2021).
Liu, X. et al. Nature 591, 627–632 (2021).
Abdul Mazid, M. et al. Nature 605, 315–324 (2022).
Li, S. et al. Cell 187, 3284–3302 (2024).
Weatherbee, B. A. T. et al. Nature 622, 584–593 (2023).
Oldak, B. et al. Nature 622, 562–573 (2023).
Sun, S. et al. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.08.05.606556 (2024).
Hislop, J. et al. Nature 626, 367–376 (2024).
Miao, Y. et al. Nature 614, 500–508 (2023).
Xue, X. et al. Nature 628, 391–399 (2024).
Li, J. et al. Cell Stem Cell 30, 362–377 (2023).
 Why researchers should use human embryo models with caution
Why researchers should use human embryo models with caution
 What is an embryo? Scientists say definition needs to change
What is an embryo? Scientists say definition needs to change
 What’s next for lab-grown human embryos?
What’s next for lab-grown human embryos?