- NEWS FEATURE
Researchers are using new molecules, engineered immune cells and gene therapy to kill senescent cells and treat age-related diseases.
By
-
Carissa Wong
-
Carissa Wong is a science journalist in London.
-
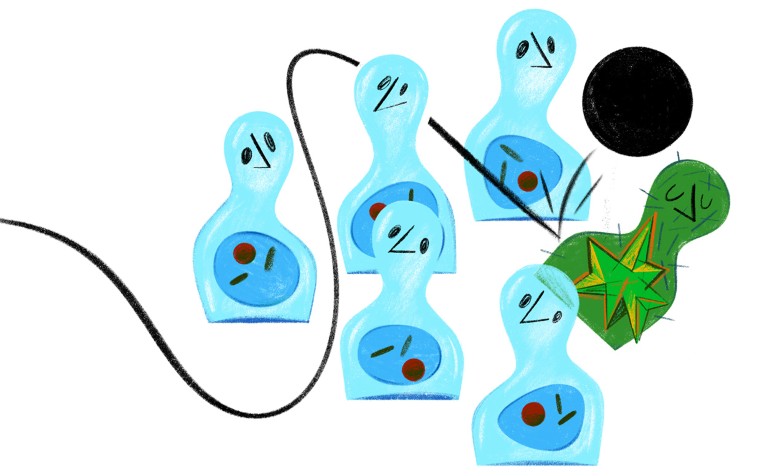
Illustration: Paweł Jońca
Lurking throughout your body, from your liver to your brain, are zombie-like entities known as senescent cells. They no longer divide or function as they once did, yet they resist death and spew out a noxious brew of biological signals that can slow cognition, increase frailty and weaken the immune system. Worst of all, their numbers increase as you age.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 629, 518-520 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-01370-4
References
Zhu, Y. et al. Aging Cell 14, 644–658 (2015).
Hayflick, L. & Moorhead, P. S. Exp. Cell Res. 25, 585–621 (1961).
Crespo-Garcia, S. et al. Nature Med. 30, 443–454 (2024).
Yousefzadeh, M. J. et al. EBioMedicine 36, 18–28 (2018).
Zhang, P. et al. Nature Neurosci. 22, 719–728 (2019).
Amor, C. et al. Nature Aging 4, 336–349 (2024).
Eskiocak, O. et al. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.19.585779 (2024).
Arora, S. et al. Med 2, 938–950 (2021).
Related Articles
-
 Why is exercise good for you? Scientists are finding answers in our cells
Why is exercise good for you? Scientists are finding answers in our cells
-
 Do cutting-edge CAR-T-cell therapies cause cancer? What the data say
Do cutting-edge CAR-T-cell therapies cause cancer? What the data say
 Hacking the immune system could slow ageing — here’s how
Hacking the immune system could slow ageing — here’s how
 To stay young, kill zombie cells
To stay young, kill zombie cells