- NEWS AND VIEWS
Two threads of research in the quest for methods that predict the 3D structures of proteins from their amino-acid sequences have become fully intertwined. The result is a leap forward in the accuracy of predictions.
By
-
Mohammed AlQuraishi
-
Mohammed AlQuraishi is in the Laboratory of Systems Pharmacology, Department of Systems Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
-
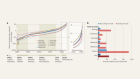
Proteins perform or catalyse nearly all chemical and mechanical processes in cells. Synthesized as linear chains of amino-acid residues, most proteins spontaneously fold into one or a small number of favoured three-dimensional structures. The sequence of amino acids specifies a protein’s structure and range of motion, which in turn determine its function. Over decades, structural biologists have experimentally determined thousands of protein structures, but the difficulty of these studies has made the promise of a computational approach for predicting protein structure from sequence alluring. Writing in Nature, Senior et al.1 describe an algorithm, AlphaFold, that takes a leap forward in solving this classic problem by bringing to bear modern machine-learning techniques.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 577, 627-628 (2020)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-03951-0
References
Senior, A. W. et al. Nature 577, 706–710 (2020).
Guvench, O. & MacKerell, A. D. Jr Methods Mol. Biol. 443, 63–88 (2008).
Maximova, T., Moffatt, R., Ma, B., Nussinov, R. & Shehu, A. PLoS Comput. Biol. 12, e1004619 (2016).
Bryngelson, J. D., Onuchic, J. N., Socci, N. D. & Wolynes, P. G. Proteins 21, 167–195 (1995).
Marks, D. S. et al. PLoS ONE 6, e28766 (2011).
Jones, D. T., Buchan, D. W. A., Cozzetto, D. & Pontil, M. Bioinformatics 28, 184–190 (2012).
Kamisetty, H., Ovchinnikov, S. & Baker, D. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 15674–15679 (2013).
Lapedes, A. S., Giraud, B. G., Liu, L. & Stormo, G. D. IMS Lecture Notes Monogr. Ser. 33, 236–256 (1999).
Wang, S., Sun, S., Li, Z., Zhang, R. & Xu, J. PLoS Comput. Biol. 13, e1005324 (2017).
Hills, R. D. & Brooks, C. L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 10, 889–905 (2009).
AlQuraishi, M. Cell Syst. 8, 292–301 (2019).
Ingraham, J., Riesselman, A., Sander, C. & Marks, D. in 7th Int. Conf. Learn. Represent. https://openreview.net/forum?id=Byg3y3C9Km (2019).
Related Articles
-
 Read the paper: Improved protein structure prediction using potentials from deep learning
Read the paper: Improved protein structure prediction using potentials from deep learning
-
 AI protein-folding algorithms solve structures faster than ever
AI protein-folding algorithms solve structures faster than ever
 Designer protein delivers signal of choice
Designer protein delivers signal of choice
 Designer proteins activate fluorescent molecules
Designer proteins activate fluorescent molecules