- NEWS AND VIEWS
Ageing is a regulated process in which hormones have pivotal roles. Crystal structures of two hormone co-receptors should be informative for drug discovery focused on age-related disorders.
By
-
Makoto Kuro-o
-
Makoto Kuro-o is in the Division of Anti-Ageing Medicine, Center for Molecular Medicine, Jichi Medical University, Shimotsuke, Tochigi 329-0498, Japan.
-
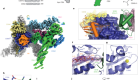
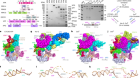
In Greek mythology, three goddesses known as the Fates govern the lifespan of each person. Klotho, Lachesis and Atropos are the spinner, the allotter and the cutter of the thread of life, respectively. So when a genetic mutation was identified in mice that undergo premature ageing1, the gene involved was fittingly named klotho. The protein it encodes, α-klotho, and a sister protein called β-klotho, are high-affinity co-receptors for certain members of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family of signalling proteins2, but their means of action has not been well characterized. Two papers3,4 online in Nature describe crystal structures of FGF–klotho complexes, not only providing a basis for understanding how klothos act, but also opening up avenues for structure-based drug design.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 553, 409-410 (2018)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-017-09032-4
References
Kuro-o, M. et al. Nature 390, 45–51 (1997).
Kurosu, H. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 6120–6123 (2006).
Chen, G. et al. Nature 553, 461–466 (2018).
Lee, S. et al. Nature 553, 501–505 (2018).
Hu, M. C., Shiizake, K., Kuro-o, M. & Moe, O. W. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 75, 503–533 (2013).
Shimada, T. et al. J. Clin. Invest. 113, 561–568 (2004).
Ogawa, Y. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 7432–7437 (2007).
Kurosu, H. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 26687–26695 (2007).
Wright, P. E. & Dyson, H. J. J. Mol. Biol. 293, 321–331 (1999).
Kuro-o, M. Nature Rev. Nephrol. 9, 650–660 (2013).
Zhang, Y. et al. eLife 1, e00065 (2012).
 Read the paper: α-Klotho is a non-enzymatic molecular scaffold for FGF23 hormone signalling
Read the paper: α-Klotho is a non-enzymatic molecular scaffold for FGF23 hormone signalling
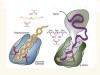 Read the paper: Structures of β-klotho reveal a ‘zip code’-like mechanism for endocrine FGF signalling
Read the paper: Structures of β-klotho reveal a ‘zip code’-like mechanism for endocrine FGF signalling
 Longer life through an odd Pol enzyme
Longer life through an odd Pol enzyme
 Mapping the path to a longer life
Mapping the path to a longer life