A near-eye display design that pairs inverse-designed metasurface waveguides with AI-driven holographic displays to enable full-colour 3D augmented reality from a compact glasses-like form factor.
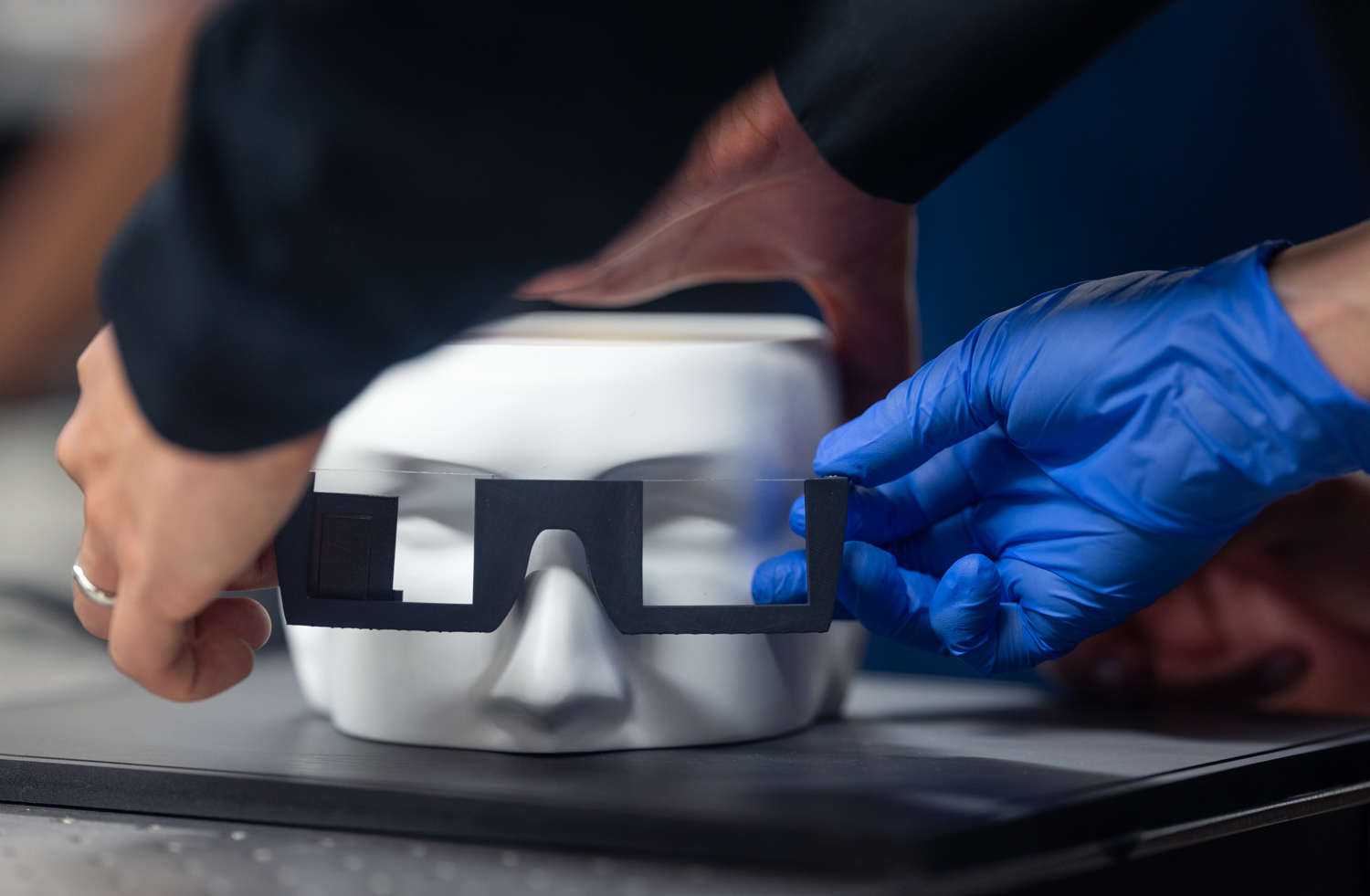

Photo by Andrew Brodhead
ABSTRACT
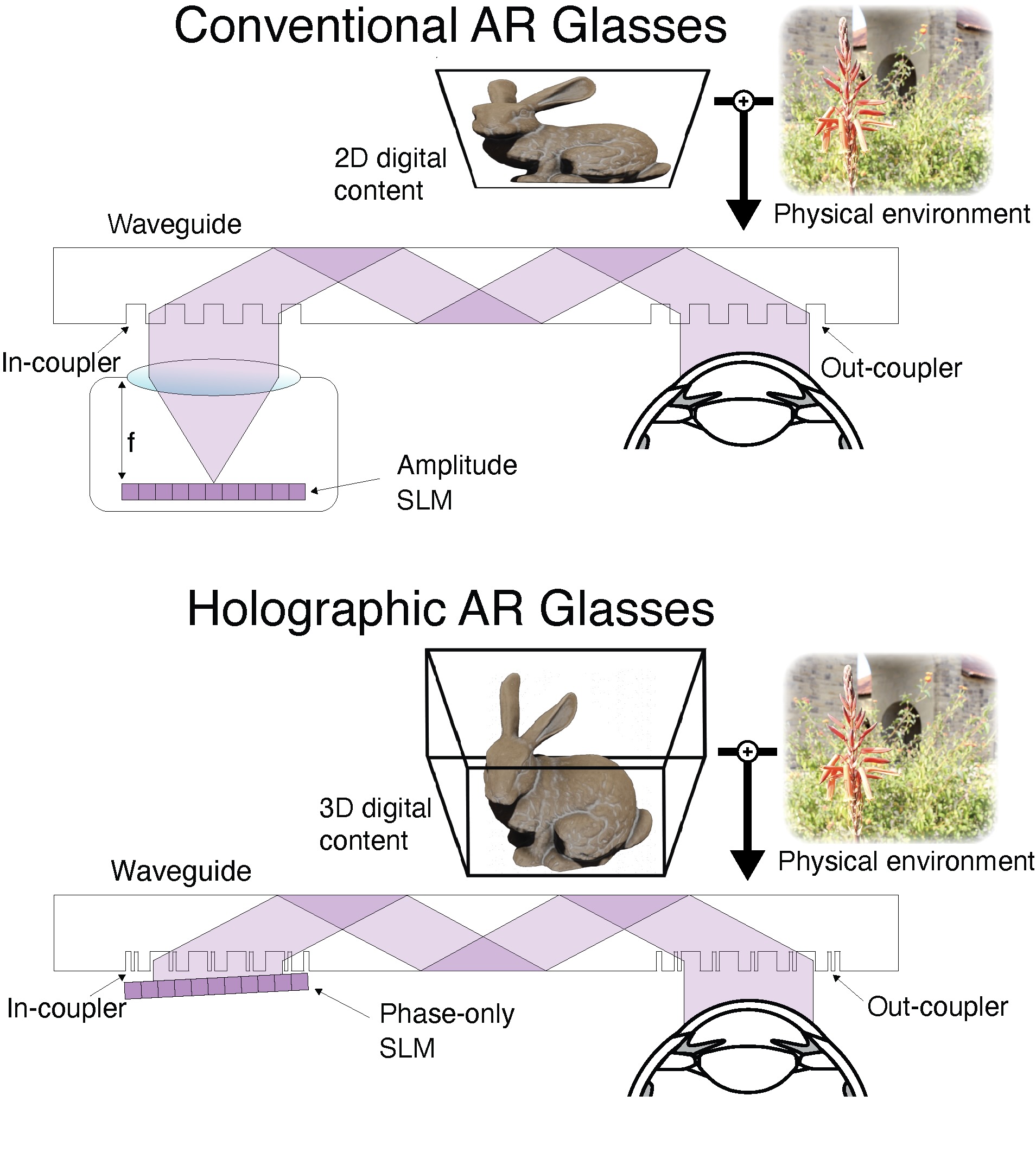
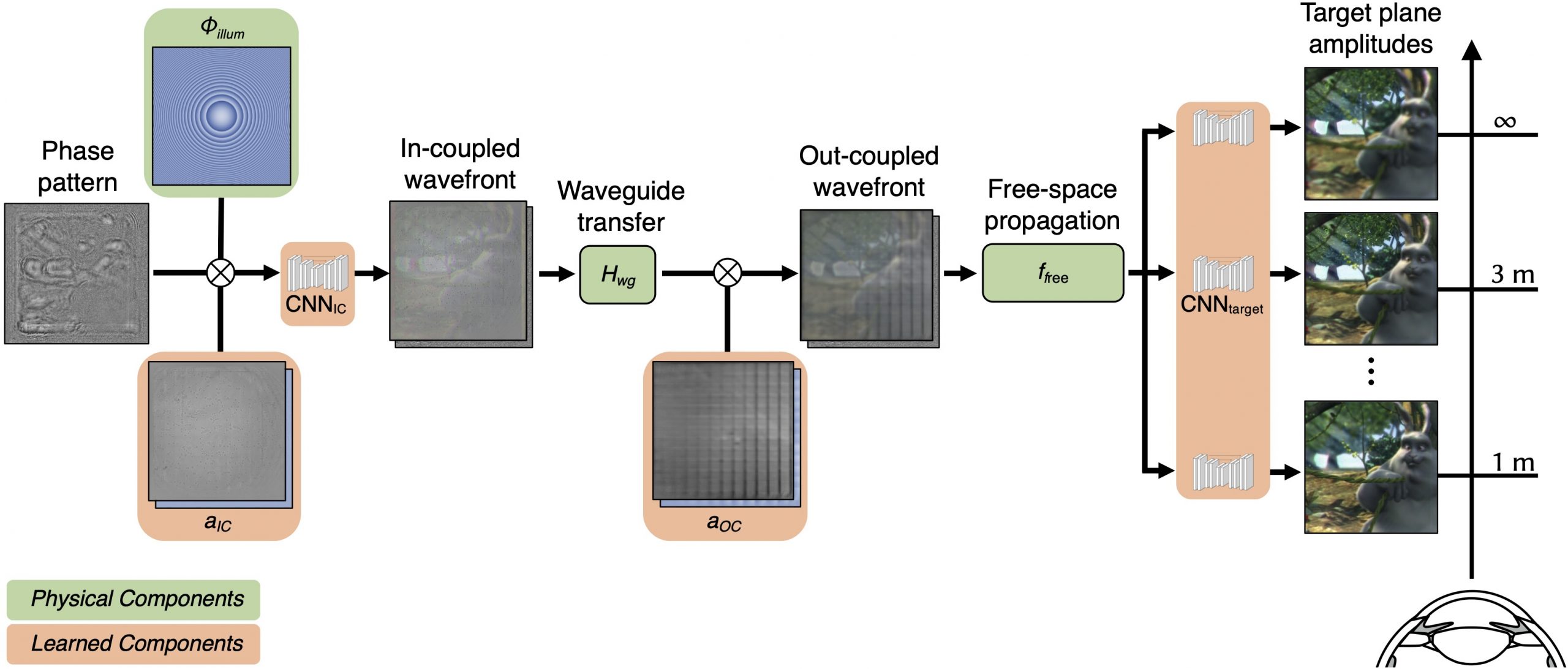
Emerging spatial computing systems seamlessly superimpose digital information on the physical environment observed by a user, enabling transformative experiences across various domains, such as entertainment, education, communication and training. However, the widespread adoption of augmented-reality (AR) displays has been limited due to the bulky projection optics of their light engines and their inability to accurately portray three-dimensional (3D) depth cues for virtual content, among other factors. Here we introduce a holographic AR system that overcomes these challenges using a unique combination of inverse-designed full-colour metasurface gratings, a compact dispersion-compensating waveguide geometry and artificial-intelligence-driven holography algorithms. These elements are co-designed to eliminate the need for bulky collimation optics between the spatial light modulator and the waveguide and to present vibrant, full-colour, 3D AR content in a compact device form factor. To deliver unprecedented visual quality with our prototype, we develop an innovative image formation model that combines a physically accurate waveguide model with learned components that are automatically calibrated using camera feedback. Our unique co-design of a nanophotonic metasurface waveguide and artificial-intelligence-driven holographic algorithms represents a significant advancement in creating visually compelling 3D AR experiences in a compact wearable device.
Comparing AR GLASSES DESIGNS
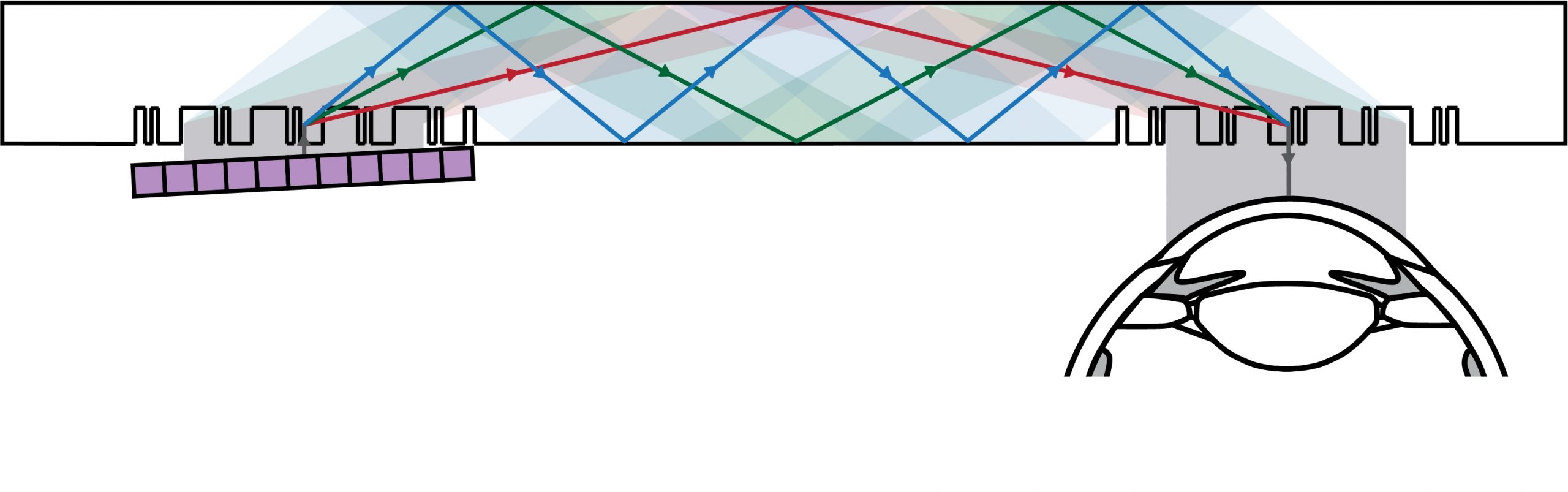
Inverse-Designed METASURFACE WAVEGUIDE
 |
|
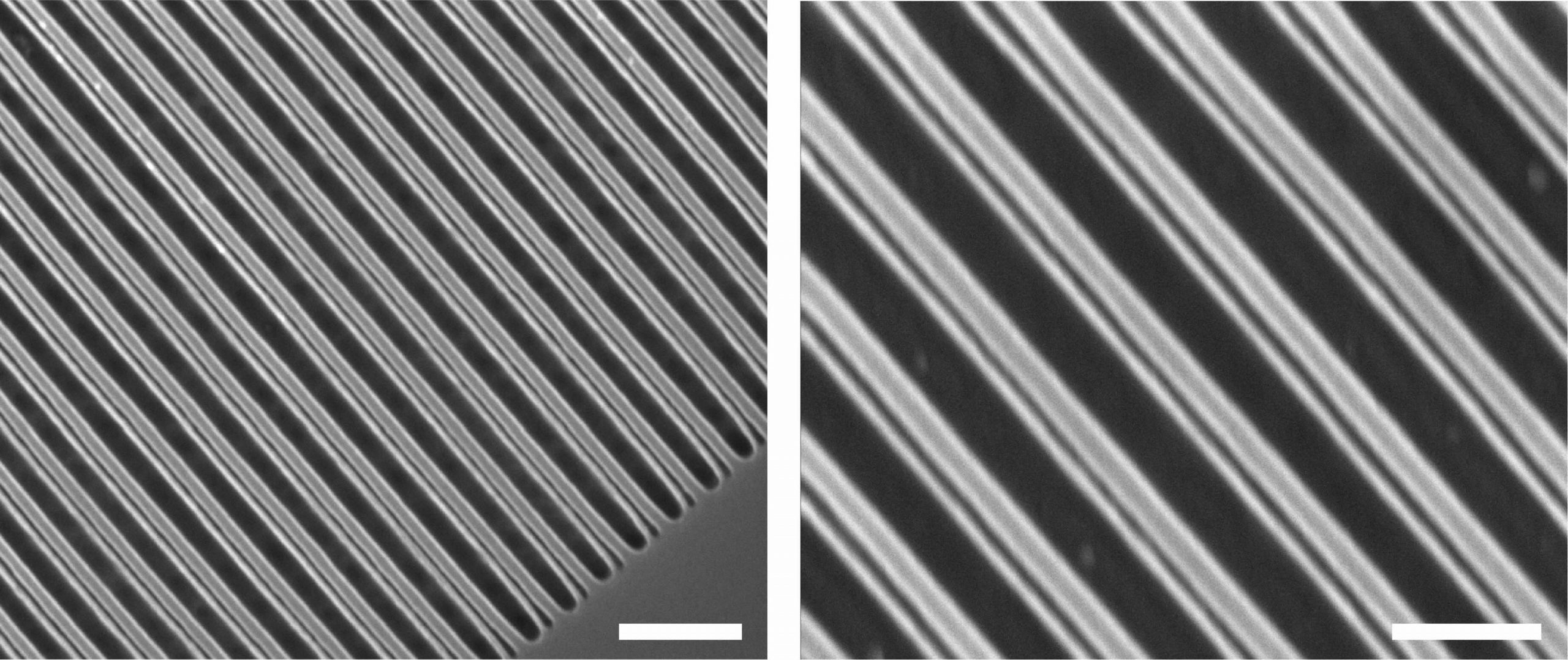
Scanning electron microscope images demonstrate the successful fabrication of our metasurface design. Scale bars: 2 μm (left), 200 nm (right). |
LEARNED PHYSICAL WAVEGUIDE MODEL
Press
Experimental Holograms
The following results are views of experimental holograms captured by a camera looking through a prototype implementation of our AR glasses design.
Notably, the components of our holographic AR glasses required to produce these holograms can fit into a wearable form factor as illustrated by the 3D-printed prototype below:

FILES
- Technical Paper (link)
- Technical Paper Supplement (link)
- Source Code (github repo)
CITATION
Gopakumar, M. et al. Full-colour 3D holographic augmented-reality displays with metasurface waveguides. Nature (2024).
BibTeX
@article{Gopakumar:2024:HolographicAR,
author = {Manu Gopakumar and Gun-Yeal Lee and Suyeon Choi and Brian Chao and Yifan Peng and Jonghyun Kim and Gordon Wetzstein},
title = {{Full-colour 3D holographic augmented-reality displays with metasurface waveguides}},
journal = {Nature},
year = {2024},
}
Related Projects
You may also be interested in related projects, where we developed AI algorithms to produce high quality 2D and 3D holograms:
- S. Choi et al. “Time-Multiplexed Neural Holography”, ACM SIGGRAPH, 2022 (link)
- S. Choi et al. “Neural 3D Holography”, ACM SIGGRAPH Asia, 2021 (link)
- Y. Peng et al. “Neural Holography”, ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2020 (link)
and holographic near-eye display designs for compact VR glasses:
- J. Kim et al. “Holographic Glasses”, SIGGRAPH, 2022 (link)
- M. Gopakumar et al. “Unfiltered Holography”, Optics Letters, 2021 (link)
Acknowledgements
M.G. is supported by a Stanford Graduate Fellowship in Science and Engineering. G.-Y.L. is supported by a Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2022R1A6A3A03073823). S.C. is supported by a Kwanjeong Scholarship and a Meta Research PhD Fellowship. B.C. is supported by a Stanford Graduate Fellowship in Science and Engineering and a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship. G.W. is supported by the ARO (PECASE Award W911NF-19-1-0120), Samsung and the Sony Research Award Program. Part of this work was performed at the Stanford Nano Shared Facilities (SNSF) and Stanford Nanofabrication Facility (SNF), supported by the National Science Foundation and the National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure under award ECCS-2026822. We also thank Y. Park for her ongoing support.
MEDIA
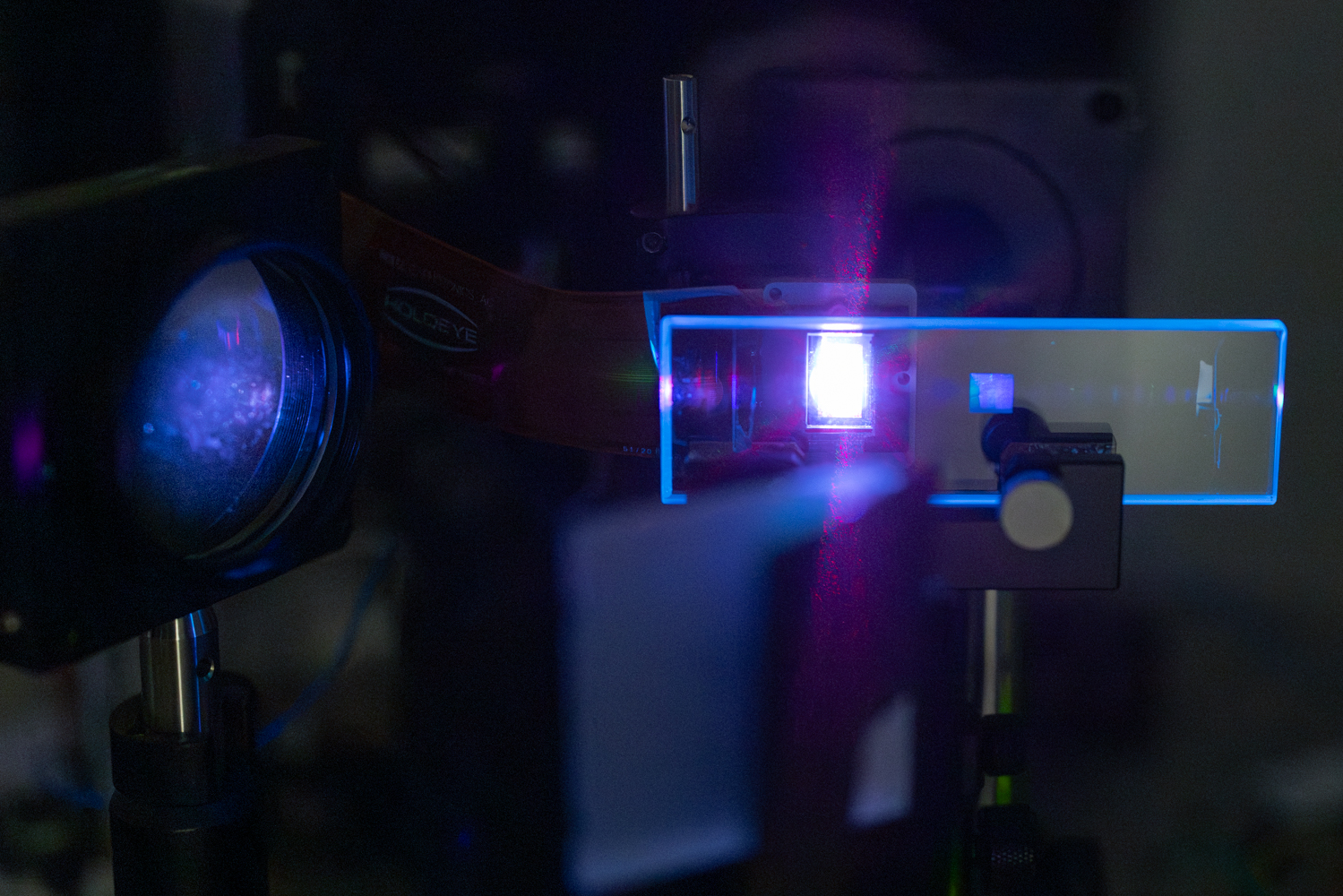 |
| Phase-modulating SLM and metasurface waveguide illuminated by a laser in the experimental setup (Photo by Andrew Brodhead). |
 |
| Research team at Stanford from left-to-right: Brian Chao, Manu Gopakumar, Gun-Yeal Lee, Gordon Wetzstein, Suyeon Choi (Photo by Andrew Brodhead). |