This blog is mainly focused on my Philosophical and theoretical ideas.
From time to time I have practical posts that are too few to deserve a blog by themselves. I still hope my other work (like above) is even more valuable than such practical article as below.
* * *
This article explains how to install Ubuntu 19.04 or similar on USB+UEFI, like you would do it on a hard drive. Regular USB install will likely fail, you need the fix below. Ubuntu installer has a bug when installing on USB using a PC that already has an UEFI boot system (like Windows 10).
Such thumb-drive is not only persistent, you can also do regular updates on it, customize the programs, repair the file-system. This is more than just a live "USB Pen Drive Linux" with persistence, it is your full Linux system in your pocket.
Only (U)EFI boot is covered here, but most recent systems support UEFI. The old BIOS boot is more complex to fix and less portable because you depend on a specific drive order.
Use this at your own risk. A single mistake might wipe out the entire hard drive on your PC.
If unsure, do a full backup of your system, including the Windows EFI partition.
P.S. The same procedure can be used to install Linux on external USB hard drive. From my experience, even an USB 2.0 hard drive with Linux is often more responsive than Linux on thumb-drive, because hard drives have very good write speed. However, a hard drive is not as portable as a small USB flash drive. If you go with flash drive, use USB 3.0 thumbdrive with a write speed of at least 30MB/s.
Optionally you can read first "Linux Grub/UEFI boot system - small howto"
Short version - for experienced users
1. Normal Ubuntu installation on USB
- format the target USB drive with "gpt" partition table (not msdos).
- create first partition fat32 of 100MB, set the flags 'esp' and 'boot'
- create second partition ext4 on the rest of the space
- use custom Ubuntu installing ("Something else"), booting in UEFI mode
- set target boot location on the USB device - like /dev/sdc, not a partition
- use the fat32 partition as 'efi'
- use the ext4 partition as '/'
- install Ubuntu
The bug is that Ubuntu installer will not install any EFI/Grub files on the USB drive, but it will put them on your first hard drive - for example in the EFI partition created by Win10. You need to move the 2 new directories to the USB drive, in the EFI partition. Normally the install will not break the existing Win10 boot.
2. Fix/Tweak the EFI/Grub on USB
- create the missing EFI directory on the (empty) USB's fat32 EFI partition
- copy recursively the directories EFI/ubuntu and EFI/Boot from your PC's EFI partition to the USB's EFI partition/directory.
- move away EFI/ubuntu and EFI/Boot from your PC's EFI directory, so you can restore your PC boot to the initial state.
Now the USB drive should also boot on other systems, and your PC will not attempt to boot Linux when the USB drive is not inserted. If you want to boot Linux, you will need to select the target USB drive from "Bios".
Detailed version - for less experienced users
new: now with pictures!
You need an installation USB drive and a target USB drive. It is easier if they are different sizes - so you can differentiate them easily
- Installation Ubuntu USB drive (like 8GB)
- Target USB drive (like 16GB - I use 32GB here)
1. Boot in UEFI mode from Ubuntu USB install stick
- enter Bios with something like Esc/F2/Fn+F2
- be sure to have "Boot Mode" to UEFI, USB Boot activated
- On Boot menu, meke the USB/Ubuntu/Linpus entry to be the first one
- Save and boot Ubuntu
- In the Ubuntu menu, use "Try Ubuntu"
2. Plug the USB stick where you want to install Ubuntu in full mode
- 16GB is a good size, USB 3.x drive+port is faster
3. Create 2 GPT partitions: first as FAT32/EFI (100MB), the rest as EXT4
- open Gparted application from the "9 dots" icon in the left/down corner (other solutions exist)
- from right/up of gparted, carefully select the destination drive (usually the last one). Double check the size to prevent formatting your main hard drive or the installation drive!!
- you may need to umount the USB stick as it is mounted automatically (Right click on partition, Umount)
- Select Device/'Create partition table'. A warning will remind you to check that you don't format the wrong drive
- Choose "gpt" type, check again, apply
- Partition/New, 'New size(MiB)'=100, 'File system'='fat32'; (optional) 'Partition name'=EFI, 'Label'=EFI; Add

- Partition/New, 'New size(MiB)'= <let it unchanged>, 'File system'='ext4'; (optional) 'Partition name'=ROOT, 'Label'=ROOT; Add
- Right click on the EFI partition; 'Manage flags'; and set the "esp" flag (this will also set 'boot'). Not sure if this is required on all systems
- Apply (click the 'V' green icon)
- Close Gparted
- (optional) Ideally shutdown the computer and remove the destination USB. Boot again the installer in "Install Ubuntu" mode, so it will not mount the destination USB. Then plug the destination USB after boot, to be seen as the last drive.
4 Install Ubuntu on target USB drive
- start the installation process; choose defaults: English/English/'I don't want to connect wi-fi'
- Leave it 'Normal installation'. I prefer to also check 'Install third-party software'...
- 'Installation type' should be 'Something else' (last at the bottom)
- Scroll until your destination USB drive (double check the size), usually it is the one at the bottom, containing the 2 partitions you created
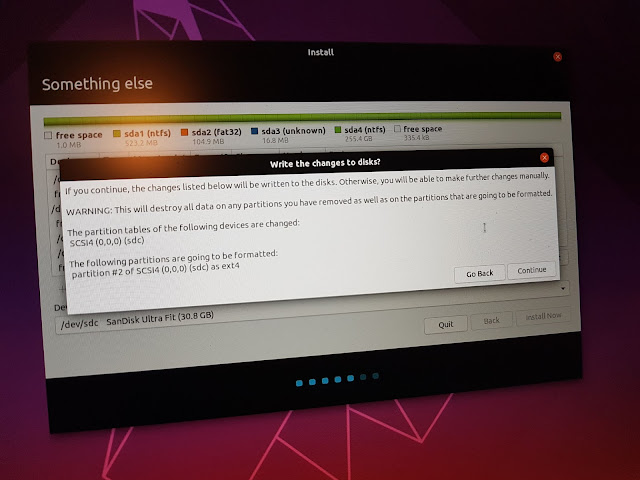
- change the bottom "Device to boot loader installation" to your target USB drive, usually the last one, like "/dev/sdc" (not the sub-partitions). Failing to do so might break the booting of you PC!
While the above setting does not work completely - it will use /dev/sda for the EFI files - just do it.
- select the ext4 partition (like /dev/sdc2), 'Change', 'Use as'='ext4', check 'Format the partition'. Double check the size to not be your hard drive; "Mount point"="/", OK
- select the EFI partition (fat32), 'Change' 'Use as'='EFI System Partition'. This might not fully work, but do your job anyway. This will at least assure that the partition will be mounted as /boot/efi in the new system.
- 'Install now'
- double check the letter of your installation disk (mine is "sdc")
- set the time zone
- choose a name, computer name, username, password
- when the installation is done, I recommend to shutdown the Ubuntu system from right/up, before unplugging the installation USB
- when the system is off or just before (re)starting, remove the installation USB
- enter Bios and activate to Boot from the USB Ubuntu drive.
- be aware that this is likely using the EFI files on your main HDD/SSD, and the USB drive is not portable yet
5. Tweak/fix the target USB to contain the right EFI files to become portable
- if the new USB drive does not boot, boot again from the installation USB, plugging the target USB after; we just need to copy couple of files to the target USB drive
- after boot, skip the customization menu for now
- open a Linux terminal, with Ctrl+Alt+T or from the left/down "9 dots" searching "terminal". I usually right click on it on the left taskbar to "Add to favorites"
- in terminal, make yourself root with "sudo su -" ; enter the password you set on installation
- run "fdisk -l" to identity the target USB disk partitions (usually the last added is at the bottom); double check the size!
- identify a previous EFI partition, from your main hard/SSD disk of your PC (probably /dev/sda2 or /dev/sda1). Check the sizes to be sure.
- create 2 directories in the local directory:
mkdir p; mkdir t
- mount the PC's EFI partition on 'p' with something like (change the partition)
mount /dev/sda2 p #your partition number might differ
- mount the EFI partition from the target USB on 't' with something like ; Note that without the installing USB drive, target USB becomes /dev/sdb instead of /dev/sdc; It might be different if you have multiple hard drives on your PC.
mount /dev/sdb1 t
- check your PC's EFI partition; you should find directories 'Boot' and 'ubuntu' along with your original 'Microsoft' directory. Beware, without the last directory, Windows will not be able to boot anymore.
ls p/EFI
- The p/ directory is likely empty, you need to copy there the directories EFI/ubuntu and EFI/Boot from the PC's EFI partition:
mkdir t/EFI
cp -a p/EFI/ubuntu t/EFI
cp -a p/EFI/Boot t/EFI
sync; umount p; umount t; sync
- Recommended, move the Linux boot directories from the PC's EFI directory. This will make the system to boot back in Windows mode until you select the USB drive in Bios.
mkdir p/OLD
mv p/EFI/ubuntu p/OLD
mv p/EFI/Boot p/OLD
Note: if Windows boot fails after installing Ubuntu, when USB is not plugged:
- this happens if you don't delete/move the Ubuntu's EFI files from the PC's EFI partition
- however, Windows EFI/boot files are there, Ubuntu files are installed along with them
- you can still select Windows from the Boot menu of your "Bios" to bypass Ubuntu/Grub boot, but the best way is to move away that Ubuntu files from the PC's EFI partition
6. Test it
- Shutdown the computer
- You should re-select in Bios to UEFI boot from the USB's EFI partition, otherwise it will boot from the Windows partition
- You can later setup network and do the updates, add more programs, etc. Each kernel update will also add grub options to boot additional operating systems (Windows), but this will only work for that PC where the update ran.
Now you should have a really portable USB thumb-drive that should boot on most EFI system; You may need to install additional video drivers for some system you want to be able to run on.
Anything you update/modify should stay persistent on this USB drive.
Try to boot it on another system, in U(EFI)/USB mode, selecting the right boot order in Bios.
Enjoy!
I hoped I added all the needed details. Let me know if it worked for you or something must be clarified. Also, please share this article if you find it interesting. Thank you.