MCP-Universe: Benchmarking Large Language Models with
Real-World Model Context Protocol Servers
MCP-Universe is a comprehensive framework designed for developing, testing, and benchmarking AI agents. It offers a robust platform for building and evaluating both AI agents and LLMs across a wide range of task environments. The framework also supports seamless integration with external MCP servers and facilitates sophisticated agent orchestration workflows.
Ziyang Luo*,
Zhiqi Shen*,
Wenzhuo Yang*,
Zirui Zhao,
Prathyusha Jwalapuram
Amrita Saha,
Doyen Sahoo,
Silvio Savarese,
Caiming Xiong,
Junnan Li
* Equal contribution
Salesforce AI Research
Contact: zluo@salesforce.com, cxiong@salesforce.com, junnan.li@salesforce.com
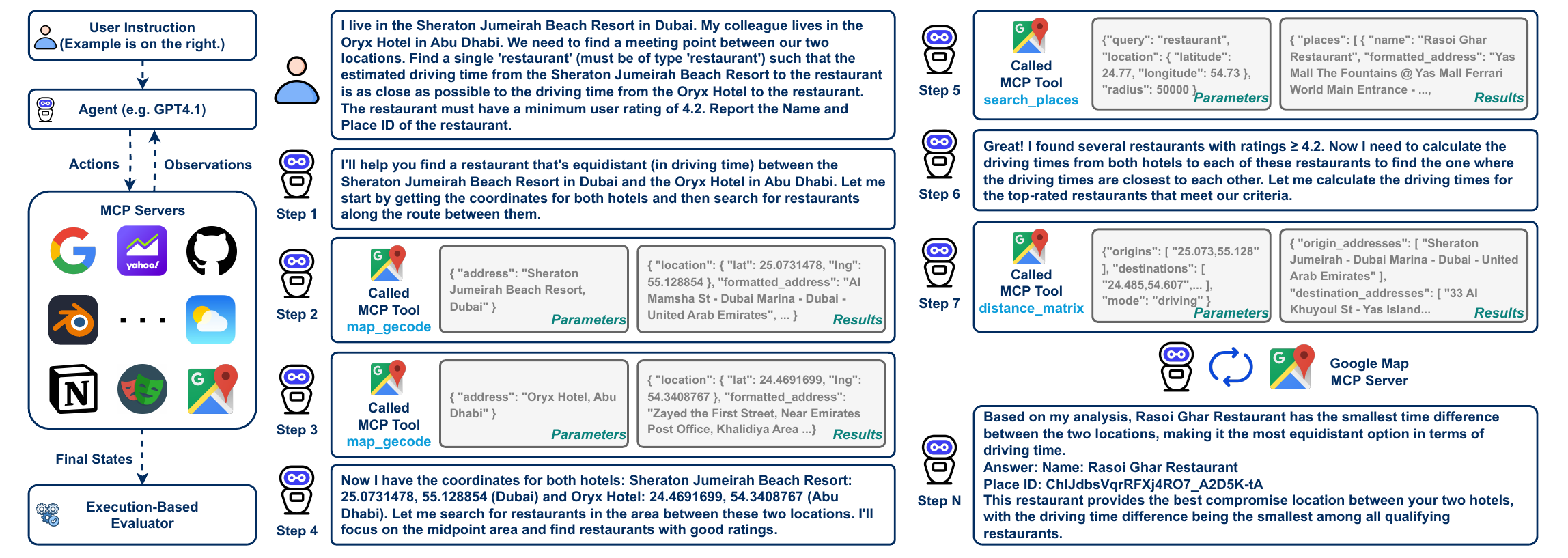
Figure 1: Example from MCP-Universe illustrating realistic challenges, including real-world tool usage, long-horizon multi-turn tool calls, long context windows, scattered evidence, and large tool spaces. Unlike prior work, MCP-Universe is grounded in real-world MCP servers connected to actual data sources and environments.
Leaderboard
Performance comparison across different LLMs and Agents on MCP-Universe benchmark. Success Rate (SR), Average Evaluator Score, and Average Steps reported.
Proprietary Model
Open-Source Model
Overall Track: Combines results from both ReAct and Function Call tracks, showing the best performance achieved by each model across both approaches. Models are ranked by their highest overall success rate from either track.
| Model | Location Navigation |
Repository Management |
Financial Analysis |
3D Designing |
Browser Automation |
Web Searching |
Average Evaluator Score |
Average Steps |
Overall Success Rate |
|---|
Performance Insights
Even SOTA models show significant limitations, with the best model (GPT-5) achieving only 43.72% overall success rate. This highlights the challenging nature of real-world MCP server interactions and the substantial room for improvement in current LLM agents. The gap between proprietary and open-source models remains substantial.
Key Findings
Long-Context Challenge
Token count increases rapidly with interaction steps, often leading to context overflow and degraded performance in multi-step tasks requiring extensive reasoning.
Unknown-Tools Challenge
LLM agents often lack familiarity with precise usage patterns, parameter specifications, and expected behaviors of diverse MCP servers.
Cross-Domain Variations
Models show markedly different success rates across application domains, suggesting domain-specific optimization needs and knowledge gaps.