Dtags: Directory Tags for Lazy Programmers
Dtags is a command-line tool that lets you tag directories for faster filesystem navigation and command execution.
Requirements
- Recent versions of Bash, Zsh or Fish
- Python 3.6+
Installation
Install via pip:
For Bash, add the following line in ~/.bashrc:
For Zsh, add the following line in ~/.zshrc:
autoload -U +X compinit && compinit autoload -U +X bashcompinit && bashcompinit source <(dtags-activate)
For Fish, add the following line in ~/.config/fish/config.fish:
dtags-activate fish | source
For Git Bash on Windows, add the following lines
in ~/.bashrc:
export DTAGS_GIT_BASH=1 source <(dtags-activate)
Restart your shell. The following commands will be available after:
tag --help untag --help tags --help d --help run --help
Tab-completion should work out-of-the-box.
Usage
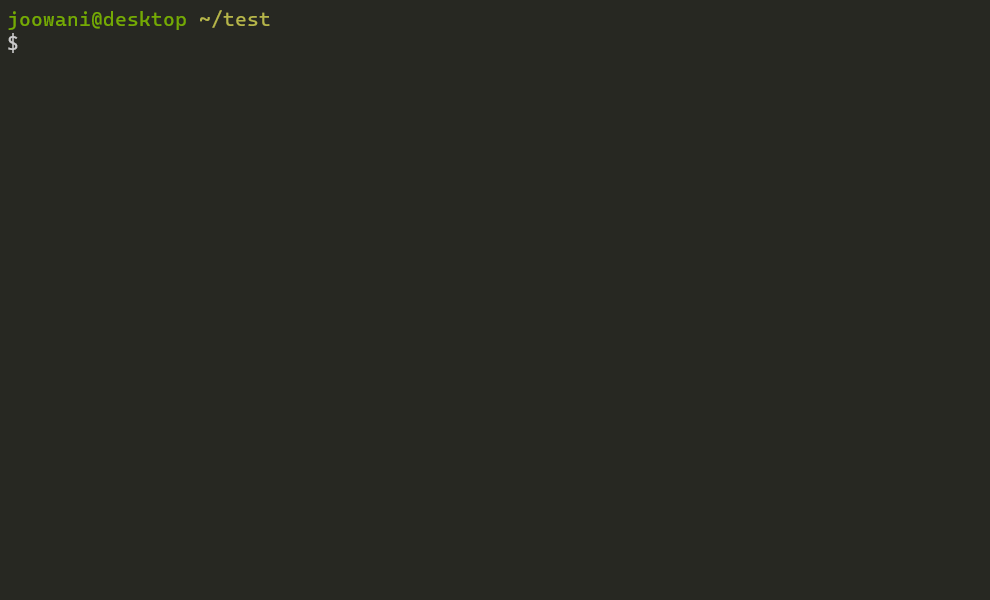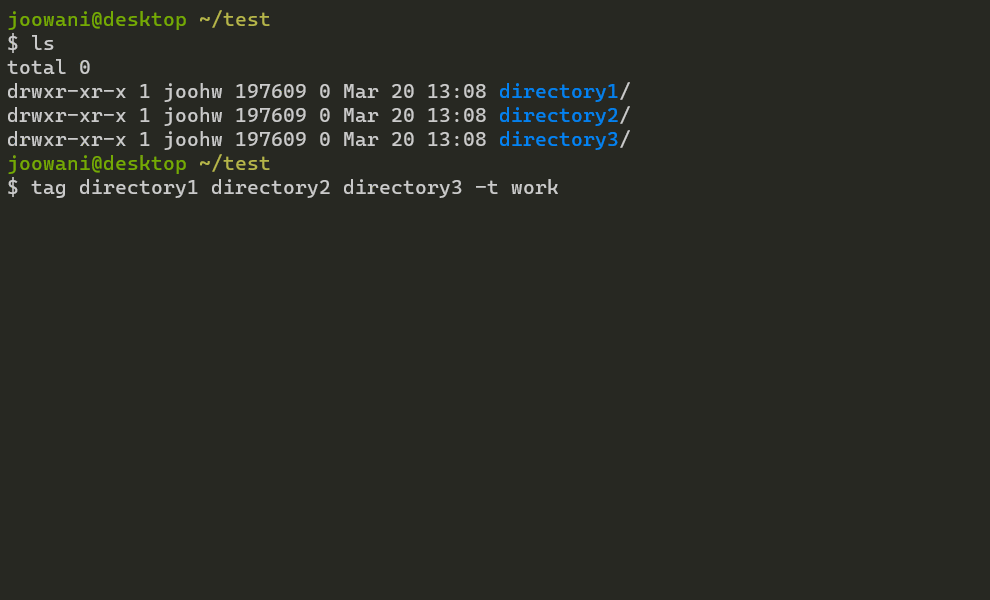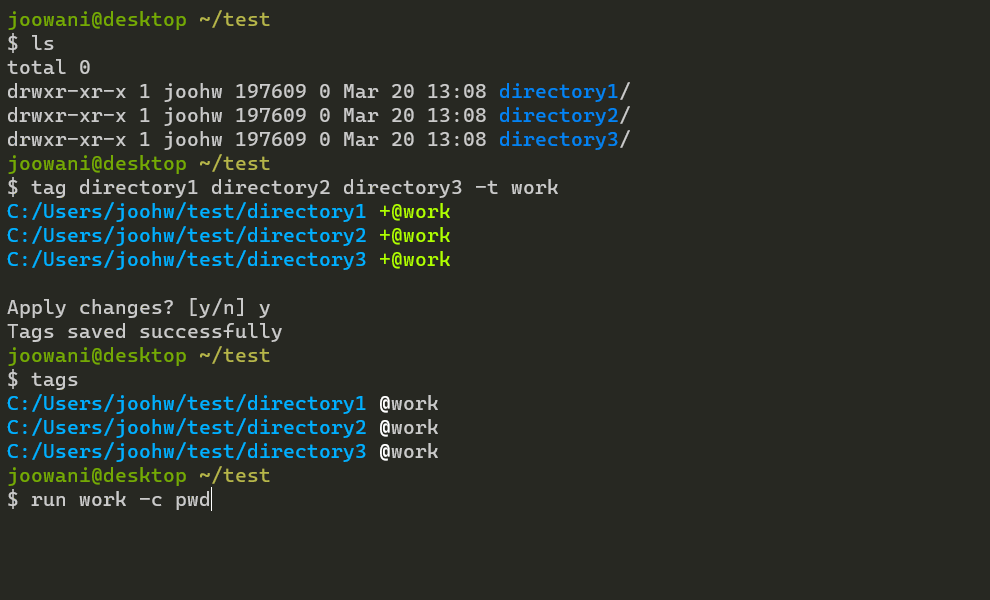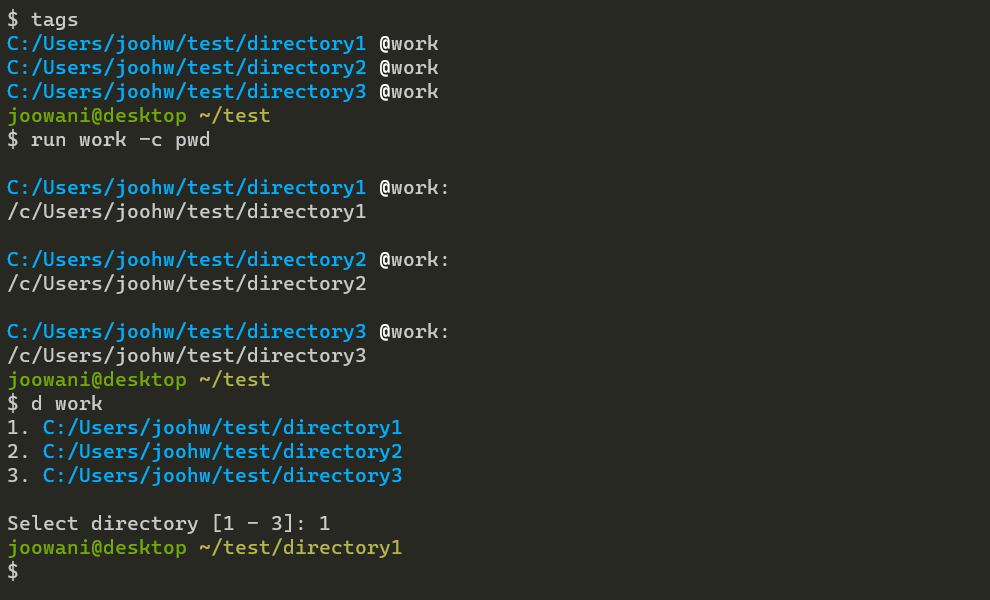
Tag directories with tag:
# Tag directory ~/foo with "work" (tags are indicated with the "@" prefix) $ tag ~/foo -t work /home/user/foo +@work # If tag names are not specified, directory basenames are used instead $ tag ~/foo /home/user/foo +@foo # Tag directories ~/bar and ~/baz with "app" and "work" (many-to-many) $ tag ~/bar ~/baz -t app work /home/user/bar +@app +@work /home/user/baz +@app +@work
Execute commands in one or more directories with run:
# Run "git status" in all directories tagged "work" $ run work -c git status # Run "git status" in directories ~/foo and ~/bar $ run ~/foo ~/bar -c git status # Mix tags and directory paths $ run work ~/foo -c git status
Change directories by path or tag with d:
# Go to directory tagged "work" # If there are multiple directories, a selection prompt is displayed $ d work # Go to directory ~/foo (works just like cd) $ d ~/foo # Use -t/--tag to always assume the argument is a tag $ d -t foo
Untag directories with untag:
# Remove tags "app" and "work" from directory ~/foo and ~/bar $ untag ~/foo ~/bar -t app work # Remove all tags from directory ~/foo $ untag ~/foo # Remove tag "app" from all directories $ untag -t app
Manage tags with tags:
# List all tags $ tags # List all tags in JSON format $ tags --json # Clean invalid directories $ tags --clean # Remove all tags $ tags --purge
Use --help to see more information on each command.
Technical Notes
- Tags are saved in
~/.dtagsdirectory (created when a dtags command is first run). - The files in
~/.dtagsare not meant to be edited manually. - By default, directory paths take precedence over tags when name collisions occur.
- Tag names are automatically slugified (e.g. "foo bar" to "foo-bar").
- Tag names are displayed with the "@" character prefix for easy identification.
- Directory paths and tag names are ordered alphabetically.
Uninstallation
Run the following commands to completely uninstall dtags:
$ pip uninstall dtags
$ rm -rf ~/.dtagsThen remove the dtags-activate line from your shell runtime configuration.