Gödel's Poetry
A recursive, reflective POETRY algorithm variant using Goedel-Prover-V2
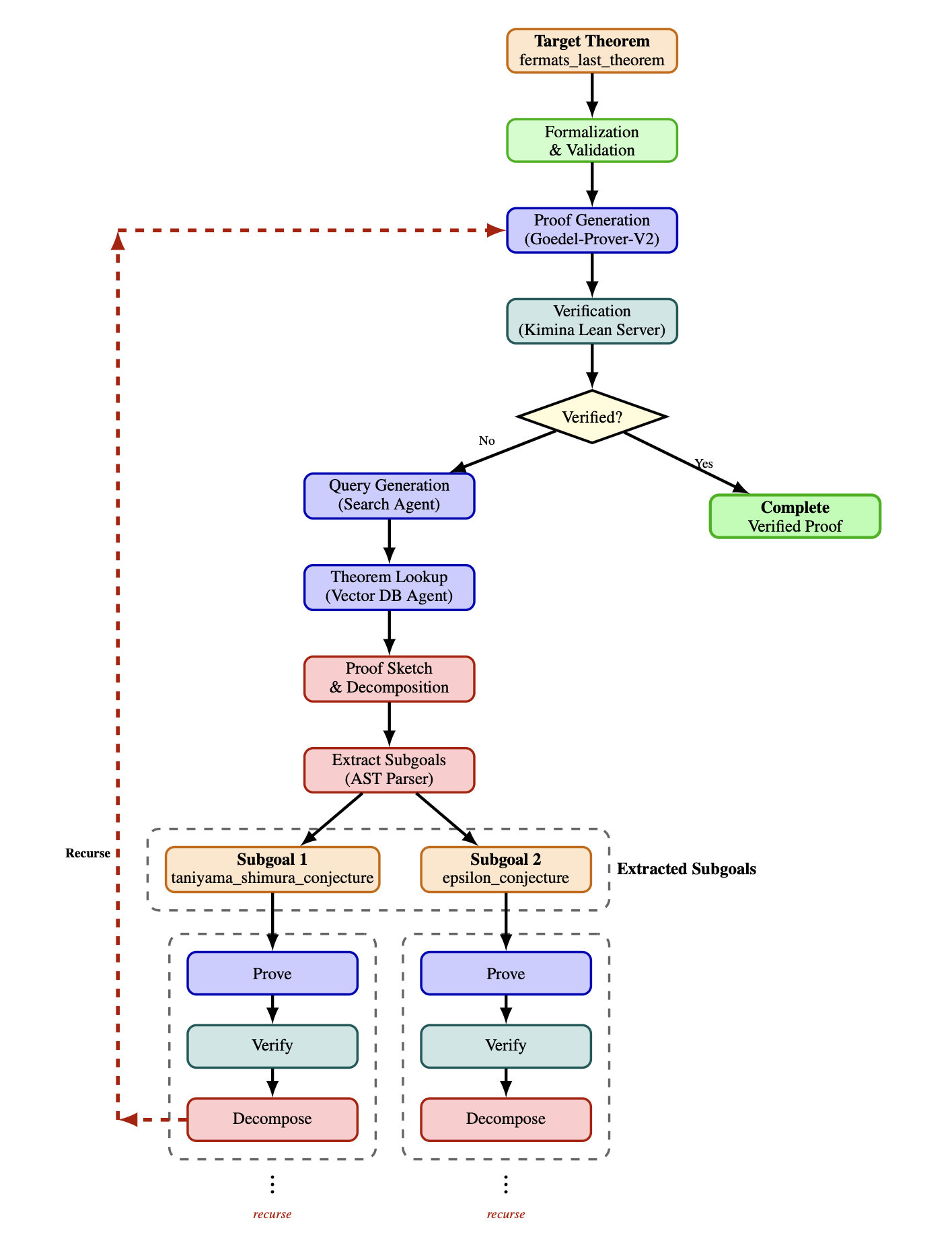
Gödel's Poetry is an advanced automated theorem proving system that combines Large Language Models (LLMs) with formal verification in Lean 4. The system takes mathematical theorems—either in informal natural language or formal Lean syntax—and automatically generates verified proofs through a sophisticated multi-agent architecture.
- Github repository: https://github.com/KellyJDavis/goedels-poetry/
- Documentation: https://KellyJDavis.github.io/goedels-poetry/
Table of Contents
What Does Gödel's Poetry Do?
Gödel's Poetry is an AI-powered theorem proving system that bridges the gap between informal mathematical reasoning and formal verification. The system:
-
Accepts theorems in multiple formats:
- Informal natural language (e.g., "Prove that the square root of 2 is irrational")
- Formal Lean 4 syntax (e.g.,
theorem sqrt_two_irrational : Irrational (√2) := by sorry)
-
Automatically generates verified proofs through a multi-agent workflow:
- Formalization: Converts informal statements into formal Lean 4 theorems
- Semantic Checking: Validates that formalizations preserve the original meaning
- Proof Generation: Creates proofs using specialized LLMs trained on Lean 4
- Verification: Validates all proofs using the Lean 4 proof assistant
- Search Query Generation: Generates queries for retrieving relevant theorems from knowledge bases
- Vector Database Querying: Queries a Lean Explore vector database to retrieve relevant theorems and lemmas
- Proof Sketching: Decomposes difficult theorems into manageable subgoals using retrieved results
- Verification: Validates sketches using the Lean 4 proof assistant
- Recursive Refinement: Recursively applies proof generation/sketching to subgoals
-
Leverages state-of-the-art technology:
- Custom fine-tuned models (Goedel-Prover-V2, Goedel-Formalizer-V2)
- Integration with frontier LLMs (GPT-5, Qwen3)
- The Kimina Lean Server for high-performance Lean 4 verification
- LangGraph for orchestrating complex multi-agent workflows
The system is designed for researchers, mathematicians, and AI practitioners interested in automated theorem proving, formal verification, and the intersection of natural and formal languages.
Quick Starts
Quick Starts assume a clean PyPI install (pip install goedels-poetry) and configuration via environment variables only. Each backend section is self-contained—pick your provider and follow the steps. If using OpenAI for any agent (including the decomposer), set the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable.
Quick Start: Ollama
- Install Gödel's Poetry
pip install goedels-poetry
- Start Ollama and pull models (once)
ollama pull kdavis/goedel-formalizer-v2:32b ollama pull kdavis/Goedel-Prover-V2:32b ollama pull qwen3:30b
- Set your OpenAI key
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-openai-key"
- Run a quick check
Quick Start: vLLM (local server on port 8002)
- Install Gödel's Poetry
pip install goedels-poetry
-
Start vLLM locally on
http://localhost:8002/v1with these models (avoid 8000/8001 used by Kimina/Lean Explore):Goedel-LM/Goedel-Formalizer-V2-32BGoedel-LM/Goedel-Prover-V2-32BQwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507
Example (multi-model) start:
python -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \ --served-model Goedel-LM/Goedel-Formalizer-V2-32B \ --served-model Goedel-LM/Goedel-Prover-V2-32B \ --served-model Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507 \ --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8002
-
Configure environment
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-openai-key" export FORMALIZER_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="vllm" export FORMALIZER_AGENT_LLM__URL="http://localhost:8002/v1" export FORMALIZER_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="Goedel-LM/Goedel-Formalizer-V2-32B" export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="vllm" export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__URL="http://localhost:8002/v1" export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="Goedel-LM/Goedel-Prover-V2-32B" export SEMANTICS_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="vllm" export SEMANTICS_AGENT_LLM__URL="http://localhost:8002/v1" export SEMANTICS_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507" export SEARCH_QUERY_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="vllm" export SEARCH_QUERY_AGENT_LLM__URL="http://localhost:8002/v1" export SEARCH_QUERY_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507"
- Run a quick check
Quick Start: OpenAI
- Install Gödel's Poetry
pip install goedels-poetry
- Configure environment
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-openai-key" export FORMALIZER_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="openai" export FORMALIZER_AGENT_LLM__URL="https://api.openai.com/v1" export FORMALIZER_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="gpt-5.2-2025-12-11" export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="openai" export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__URL="https://api.openai.com/v1" export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="gpt-5.2-2025-12-11" export SEMANTICS_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="openai" export SEMANTICS_AGENT_LLM__URL="https://api.openai.com/v1" export SEMANTICS_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="gpt-5.2-2025-12-11" export SEARCH_QUERY_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="openai" export SEARCH_QUERY_AGENT_LLM__URL="https://api.openai.com/v1" export SEARCH_QUERY_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="gpt-5.2-2025-12-11"
- Run a quick check
Quick Start: LM Studio
- Install Gödel's Poetry
pip install goedels-poetry
-
Start LM Studio with the OpenAI-compatible server enabled (default
http://localhost:1234/v1) and load/download these models in the UI:mradermacher/Goedel-Formalizer-V2-32B-GGUFmradermacher/Goedel-Prover-V2-32B-GGUFlmstudio-community/Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507-GGUF
-
Configure environment
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-openai-key" export FORMALIZER_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="lmstudio" export FORMALIZER_AGENT_LLM__URL="http://localhost:1234/v1" export FORMALIZER_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="mradermacher/Goedel-Formalizer-V2-32B-GGUF" export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="lmstudio" export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__URL="http://localhost:1234/v1" export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="mradermacher/Goedel-Prover-V2-32B-GGUF" export SEMANTICS_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="lmstudio" export SEMANTICS_AGENT_LLM__URL="http://localhost:1234/v1" export SEMANTICS_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="lmstudio-community/Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507-GGUF" export SEARCH_QUERY_AGENT_LLM__PROVIDER="lmstudio" export SEARCH_QUERY_AGENT_LLM__URL="http://localhost:1234/v1" export SEARCH_QUERY_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="lmstudio-community/Qwen3-30B-A3B-Instruct-2507-GGUF"
- Run a quick check
Running the Kimina Lean Server
The Kimina Lean Server is required for Gödel's Poetry to verify Lean 4 proofs. It provides high-performance parallel proof checking.
Option 1: Install from PyPI (Recommended)
The easiest way to install and run the Kimina Lean Server is via PyPI:
-
Install the server package:
pip install kimina-ast-server
-
Set up the Lean workspace (installs Lean 4, mathlib4, and dependencies):
Run the setup command to automatically install and configure everything:
# Setup in current directory kimina-ast-server setup # Or setup in a specific directory kimina-ast-server setup --workspace ~/lean-workspace # Setup and save configuration to .env file kimina-ast-server setup --workspace ~/lean-workspace --save-config
This will automatically:
- Install Elan (the Lean version manager)
- Install Lean 4 (default version v4.15.0)
- Clone and build the Lean REPL
- Clone and build the AST export tool
- Clone and build mathlib4 (Lean's math library)
⚠️ Note: This process can take 15-30 minutes depending on your system, primarily due to building mathlib4. -
Start the server:
# If you ran setup in current directory kimina-ast-server # Or if workspace is elsewhere, set the environment variable first export LEAN_SERVER_WORKSPACE=~/lean-workspace kimina-ast-server # You can also use the explicit run command kimina-ast-server run
The server will start on
http://0.0.0.0:8000by default. -
Verify the server is running (in a new terminal):
curl --request POST \ --url http://localhost:8000/api/check \ --header 'Content-Type: application/json' \ --data '{ "codes": [{"custom_id": "test", "proof": "#check Nat"}], "infotree_type": "original" }' | jq
You can also visit
http://localhost:8000/docsfor interactive API documentation.
Install from Source
If you prefer to install from source, please refer to the Kimina Lean Server repository for detailed installation instructions.
Alternative: Docker (Production)
For production deployments, you can use Docker. See the Kimina Server README for Docker deployment options.
Running the Lean Explore Server
The Lean Explore Server is required for Gödel's Poetry to query the vector database for relevant theorems and lemmas. It provides semantic search capabilities across Lean 4 declarations.
Option 1: Install from PyPI (Recommended)
The easiest way to install and run the Lean Explore Server is via PyPI:
-
Install the server package:
-
Download local data:
This downloads the database, embeddings, and search index needed for local searches. This step is required for the local backend.
⚠️ Note: The local backend must be used (not the remote API) because the remote API uses a Mathlib version incompatible with that required by Gödel's Poetry. -
Start the HTTP server:
leanexplore http serve --backend localThe server will start on
http://localhost:8001/api/v1by default. -
Verify the server is running (in a new terminal):
curl --request POST \ --url http://localhost:8001/api/v1/search \ --header 'Content-Type: application/json' \ --data '{"query": "natural numbers", "package_filters": ["Mathlib"]}' | jq
You can also visit
http://localhost:8001/docsfor interactive API documentation (if available).
Install from Source
If you prefer to install from source, please refer to the Lean Explore repository for detailed installation instructions.
For more information, see the Lean Explore documentation.
Using the Command Line Tool
Once installed, you can use the goedels_poetry command to prove theorems:
Prove a Single Formal Theorem
goedels_poetry --formal-theorem "import Mathlib\n\nopen BigOperators\n\ntheorem theorem_54_43 : 1 + 1 = 2 := by sorry"Formal theorems supplied on the command line (or via files) must include their full Lean preamble—imports, options, namespaces, and any comments required to state the theorem. Gödel's Poetry no longer prepends the default header for user-supplied formal problems. (The default header is still added automatically when an informal theorem is formalized by the system.)
Prove a Single Informal Theorem
goedels_poetry --informal-theorem "Prove that the sum of two even numbers is even"Batch Process Multiple Theorems
Process all .lean files in a directory:
goedels_poetry --formal-theorems ./my-theorems/
Process all .txt files containing informal theorems:
goedels_poetry --informal-theorems ./informal-theorems/
For batch processing, the tool will:
- Read each theorem from its file
- Attempt to generate and verify a proof
- Save results to
.prooffiles (for successful proofs) or.failed-prooffiles (for failed proofs, validation failures, or errors) alongside the originals
Get Help
Enable Debug Mode
To see detailed LLM and Kimina server responses during execution, set the GOEDELS_POETRY_DEBUG environment variable:
On Linux/macOS:
export GOEDELS_POETRY_DEBUG=1 goedels_poetry --formal-theorem "import Mathlib\n\nopen BigOperators\n\ntheorem theorem_54_43 : 1 + 1 = 2 := by sorry"
On Windows (Command Prompt):
set GOEDELS_POETRY_DEBUG=1 goedels_poetry --formal-theorem "import Mathlib\n\nopen BigOperators\n\ntheorem theorem_54_43 : 1 + 1 = 2 := by sorry"
On Windows (PowerShell):
$env:GOEDELS_POETRY_DEBUG=1 goedels_poetry --formal-theorem "import Mathlib`n`nopen BigOperators`n`ntheorem theorem_54_43 : 1 + 1 = 2 := by sorry"
When debug mode is enabled, all responses from:
- FORMALIZER_AGENT_LLM - Formalization responses
- PROVER_AGENT_LLM - Proof generation responses
- SEMANTICS_AGENT_LLM - Semantic checking responses
- SEARCH_QUERY_AGENT_LLM - Search query generation responses
- DECOMPOSER_AGENT_LLM - Proof sketching/decomposition responses
- KIMINA_SERVER - Lean 4 verification and AST parsing responses
- LEAN_EXPLORE_SERVER - Vector database search responses
will be printed to the console with rich formatting for easy debugging and inspection.
Examples
Example 1: Simple Arithmetic
goedels_poetry --formal-theorem \
"import Mathlib\n\nopen BigOperators\n\ntheorem add_comm_example : 3 + 5 = 5 + 3 := by sorry"Example 2: Informal Theorem
goedels_poetry --informal-theorem \
"Prove that for any natural numbers a and b, a + b = b + a"Example 3: Batch Processing
Create a directory with theorem files:
mkdir theorems cat <<'EOF' > theorems/test1.lean import Mathlib open BigOperators theorem test1 : 2 + 2 = 4 := by sorry EOF cat <<'EOF' > theorems/test2.lean import Mathlib open BigOperators theorem test2 : 5 * 5 = 25 := by sorry EOF goedels_poetry --formal-theorems ./theorems/
Results will be saved as test1.proof and test2.proof.
How It Works
Gödel's Poetry orchestrates a set of specialized agents over OpenAI-compatible LLM endpoints plus two external services (Kimina Lean Server and Lean Explore). The flow depends on whether the input is informal or already formal Lean.
Core loop (formal theorems)
- Prover Agent tries to solve the Lean theorem with the configured prover LLM.
- Proof Checker verifies the proof via Kimina; failures trigger self-correction and retry limits.
Informal path (adds formalization)
- Formalizer Agent converts natural language to Lean.
- Syntax & Semantics Checks ensure the formal statement matches intent (Semantics Agent).
- Then the core loop proceeds as above.
Decomposition for hard problems
- Vector Search (when needed) uses the Search Query agent + Lean Explore to fetch related lemmas.
- Decomposer sketches a proof and splits it into subgoals using lemmas found via vector search.
- Subgoals are proved recursively with the Prover + Proof Checker cycle.
- Successful subproofs are merged into the final Lean proof.
Providers and endpoints
- LLMs use OpenAI-compatible endpoints from Ollama, vLLM, LM Studio, or OpenAI (one set of env vars per agent).
- All agents, including the decomposer, can use any supported provider (Ollama, vLLM, LM Studio, or OpenAI).
- When using OpenAI, set the
OPENAI_API_KEYenvironment variable. - Kimina Lean Server verifies proofs; Lean Explore provides vector search. These can be remote as long as URLs are set.
Developer Guide
Development Setup
-
Clone and install with development dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/KellyJDavis/goedels-poetry.git cd goedels-poetry make installThis will:
- Create a virtual environment using
uv - Install all dependencies
- Set up pre-commit hooks for code quality
- Create a virtual environment using
-
Activate the environment (if needed):
source .venv/bin/activate # Linux/macOS .venv\Scripts\activate # Windows
Testing
The project includes comprehensive unit and integration tests.
Unit Tests Only (Fast)
This runs all tests except those requiring Lean installation.
Integration Tests (Requires Lean Server)
Integration tests verify the Kimina Lean Server integration. These tests require a running Kimina Lean server.
First-time setup:
You can set up the Kimina server using the PyPI package (recommended):
# Install integration test dependencies uv sync # Install Kimina server from PyPI pip install kimina-ast-server # Set up Lean workspace (installs Lean 4, mathlib4, and dependencies - takes 15-30 minutes) kimina-ast-server setup # Or setup in a specific directory kimina-ast-server setup --workspace ~/lean-workspace
If you prefer to install from source, please refer to the Kimina Lean Server repository for detailed installation instructions.
Run integration tests:
# Terminal 1: Start the Kimina server kimina-ast-server # Or if workspace is in a different location export LEAN_SERVER_WORKSPACE=~/lean-workspace kimina-ast-server # Terminal 2: Run the tests cd ../goedels-poetry make test-integration
The tests will automatically connect to http://localhost:8000. To use a different URL:
export KIMINA_SERVER_URL=http://localhost:9000
make test-integrationNote: Integration tests require Python 3.10+ and a running Lean server with proper REPL configuration.
All Tests
This runs both unit and integration tests sequentially.
Makefile Targets
The repository provides several convenient Make targets:
| Target | Description |
|---|---|
make install |
Install the virtual environment and pre-commit hooks |
make check |
Run all code quality checks (linting, type checking, dependency audit) |
make test |
Run unit tests with coverage (excludes integration tests) |
make test-integration |
Run integration tests (requires Lean installation) |
make test-all |
Run all tests (unit + integration) |
make build |
Build wheel distribution package |
make clean-build |
Remove build artifacts |
make publish |
Publish to PyPI (requires credentials) |
make docs |
Build and serve documentation locally |
make docs-test |
Test documentation build without serving |
make help |
Display all available targets with descriptions |
Code Quality Tools
The make check target runs:
- uv lock - Ensures lock file consistency
- pre-commit - Runs linting and formatting (Ruff)
- mypy - Static type checking
- deptry - Checks for obsolete dependencies
Configuration
Default Configuration Parameters
Configuration is stored in goedels_poetry/data/config.ini:
[FORMALIZER_AGENT_LLM] model = kdavis/goedel-formalizer-v2:32b provider = ollama url = http://localhost:11434/v1 max_tokens = 50000 num_ctx = 40960 max_retries = 10 max_remote_retries = 5 [PROVER_AGENT_LLM] model = kdavis/Goedel-Prover-V2:32b provider = ollama url = http://localhost:11434/v1 max_tokens = 50000 num_ctx = 40960 max_self_correction_attempts = 2 max_depth = 20 max_pass = 32 max_remote_retries = 5 [SEMANTICS_AGENT_LLM] model = qwen3:30b provider = ollama url = http://localhost:11434/v1 max_tokens = 50000 num_ctx = 262144 max_remote_retries = 5 [SEARCH_QUERY_AGENT_LLM] model = qwen3:30b provider = ollama url = http://localhost:11434/v1 max_tokens = 50000 num_ctx = 262144 max_remote_retries = 5 [DECOMPOSER_AGENT_LLM] model = gpt-5.2-2025-12-11 provider = openai url = https://api.openai.com/v1 max_tokens = 50000 max_remote_retries = 5 max_self_correction_attempts = 6 [KIMINA_LEAN_SERVER] url = http://0.0.0.0:8000 max_retries = 5 [LEAN_EXPLORE_SERVER] url = http://localhost:8001/api/v1 package_filters = Mathlib,Batteries,Std,Init,Lean
Configuration Parameters Explained
Formalizer Agent:
model: The LLM used to convert informal theorems to Lean 4provider: Backend provider (ollama,vllm,lmstudio, oropenai)url: Base URL for the provider API (required for non-OpenAI providers)max_tokens: Maximum tokens in a generated responsenum_ctx: Context window size (tokens)max_retries: Maximum attempts to formalize a theoremmax_remote_retries: Maximum remote API retry attempts for network/API errors
Prover Agent:
model: The LLM used to generate proofsprovider: Backend provider (ollama,vllm,lmstudio, oropenai)url: Base URL for the provider API (required for non-OpenAI providers)max_tokens: Maximum tokens in a generated responsenum_ctx: Context window size (tokens)max_self_correction_attempts: Maximum proof generation self-correction attemptsmax_depth: Maximum recursion depth for proof decompositionmax_pass: Maximum number of proof attempts before triggering decompositionmax_remote_retries: Maximum remote API retry attempts for network/API errors
Semantics Agent:
model: The LLM used to validate semantic equivalenceprovider: Backend provider (ollama,vllm,lmstudio, oropenai)url: Base URL for the provider API (required for non-OpenAI providers)max_tokens: Maximum tokens in a generated responsenum_ctx: Context window size (tokens)max_remote_retries: Maximum remote API retry attempts for network/API errors
Search Query Agent:
model: The LLM used to generate search queries for vector database retrievalprovider: Backend provider (ollama,vllm,lmstudio, oropenai)url: Base URL for the provider API (required for non-OpenAI providers)max_tokens: Maximum tokens in a generated responsenum_ctx: Context window size (tokens)max_remote_retries: Maximum remote API retry attempts for network/API errors
Decomposer Agent:
provider: The provider type -"ollama","vllm","lmstudio", or"openai"(default:"openai")model: The model used for proof sketching (default:gpt-5.2-2025-12-11for OpenAI)url: The base URL for the API endpoint (default:https://api.openai.com/v1for OpenAI)max_tokens: Maximum tokens in generated response (preferred overmax_completion_tokens)max_remote_retries: Maximum remote API retry attempts for network/API errorsmax_self_correction_attempts: Maximum decomposition self-correction attemptsnum_ctx: Context window size (only used whenprovider != "openai", optional)
Optional provider-specific settings (commented out in config.ini): use_beam_search, best_of, top_k, repetition_penalty, length_penalty for vLLM, and ttl for LM Studio.
Note: The api_key parameter is no longer required in configuration. For OpenAI, set the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable. For other providers, API keys are automatically derived from the provider setting.
Kimina Lean Server:
url: Server endpoint for Lean verificationmax_retries: Maximum retry attempts for server requests
Lean Explore Server:
url: Server endpoint for the Lean Explore vector databasepackage_filters: Comma-separated list of package names to filter search results (e.g., "Mathlib,Batteries,Std,Init,Lean")
Overriding Configuration with Environment Variables
The recommended way to customize configuration is using environment variables. This approach doesn't require modifying files and works great for different environments (development, testing, production):
Format: SECTION__OPTION (double underscore separator, uppercase)
Examples:
# Use a different prover model export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="custom-model:latest" # Change the Kimina server URL export KIMINA_LEAN_SERVER__URL="http://localhost:9000" # Change the Lean Explore server URL export LEAN_EXPLORE_SERVER__URL="http://localhost:8002/api/v1" # Change package filters for vector database searches export LEAN_EXPLORE_SERVER__PACKAGE_FILTERS="Mathlib,Batteries" # Use a smaller context window for faster testing export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__NUM_CTX="8192" # Run with custom configuration goedels_poetry --formal-theorem "import Mathlib\n\nopen BigOperators\n\ntheorem theorem_54_43 : 1 + 1 = 2 := by sorry"
Multiple overrides:
export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="kdavis/Goedel-Prover-V2:70b" export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__MAX_SELF_CORRECTION_ATTEMPTS="3" export PROVER_AGENT_LLM__MAX_PASS="64" export DECOMPOSER_AGENT_LLM__MODEL="gpt-5-pro" export KIMINA_LEAN_SERVER__MAX_RETRIES="10" # Provide the full preamble plus theorem body when invoking formal problems goedels_poetry --formal-theorem "import Mathlib\n\nopen BigOperators\n\ntheorem theorem_54_43 : 1 + 1 = 2 := by sorry"
Environment variables are optional - if not set, the system uses values from config.ini.
For more details and advanced configuration options, see CONFIGURATION.md.
Alternative: Modifying config.ini Directly
If you prefer, you can still modify the configuration file directly:
# Find the installation path uv run python -c "import goedels_poetry; print(goedels_poetry.__file__)" # Edit the config.ini in the installation directory # Typically: .venv/lib/python3.x/site-packages/goedels_poetry/data/config.ini
Note: Direct file changes persist until you reinstall or update the package, while environment variables are more flexible and don't require reinstallation.
Contributing
We welcome contributions! Please see CONTRIBUTING.md for detailed guidelines.
Quick contribution workflow:
- Fork the repository
- Clone your fork:
git clone git@github.com:YOUR_NAME/goedels-poetry.git - Install development environment:
make install - Create a feature branch:
git checkout -b feature-name - Make your changes and add tests
- Run quality checks:
make check - Run tests:
make test - Commit with descriptive messages
- Push and create a pull request
Code quality requirements:
- All tests must pass (
make test) - Code must pass linting and type checking (
make check) - New features should include tests and documentation
- Follow the existing code style and conventions
Project Structure
goedels-poetry/
├── goedels_poetry/ # Main package
│ ├── agents/ # Multi-agent system components
│ │ ├── formalizer_agent.py
│ │ ├── prover_agent.py
│ │ ├── proof_checker_agent.py
│ │ ├── search_query_agent.py
│ │ ├── vector_db_agent.py
│ │ ├── sketch_*.py # Proof sketching agents
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── config/ # Configuration management
│ ├── data/ # Prompts and config files
│ │ ├── config.ini
│ │ └── prompts/
│ ├── parsers/ # AST parsing utilities
│ ├── cli.py # Command-line interface
│ ├── framework.py # Core orchestration logic
│ └── state.py # State management
├── tests/ # Test suite
├── Makefile # Development automation
├── pyproject.toml # Package configuration
├── CHANGELOG.md # Version history
└── README.md # This file
Note: The Kimina Lean Server is a separate repository that must be installed and run independently.
License
This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0. See the LICENSE file for details.
Acknowledgments
- Kimina Lean Server: Built on Project Numina's excellent Lean verification server
- Lean 4: The formal verification system that powers proof checking
- LangChain & LangGraph: Frameworks for LLM orchestration
- Mathlib4: Comprehensive mathematics library for Lean
Citation
If you use Gödel's Poetry in your research, please cite:
@misc{davis2025godelspoetry, title={G\"odel's Poetry}, author={Kelly J. Davis}, year={2025}, eprint={2512.14252}, archivePrefix={arXiv}, primaryClass={cs.AI}, url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.14252}, }
For the Kimina Lean Server:
@misc{santos2025kiminaleanservertechnical, title={Kimina Lean Server: Technical Report}, author={Marco Dos Santos and Haiming Wang and Hugues de Saxcé and Ran Wang and Mantas Baksys and Mert Unsal and Junqi Liu and Zhengying Liu and Jia Li}, year={2025}, eprint={2504.21230}, archivePrefix={arXiv}, primaryClass={cs.LO}, url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.21230} }
For LeanExplore:
@misc{asher2025leanexploresearchenginelean, title={LeanExplore: A search engine for Lean 4 declarations}, author={Justin Asher}, year={2025}, eprint={2506.11085}, archivePrefix={arXiv}, primaryClass={cs.SE}, url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.11085}, }
Support
- Issues: Report bugs or request features at GitHub Issues
- Discussions: Ask questions at GitHub Discussions
- Documentation: Visit the official docs
Ready to prove some theorems? 🚀
goedels_poetry --informal-theorem "Prove that the sum of the first n natural numbers equals n(n+1)/2"