Stage 1: Masked SFT on High-Quality Reasoning Traces
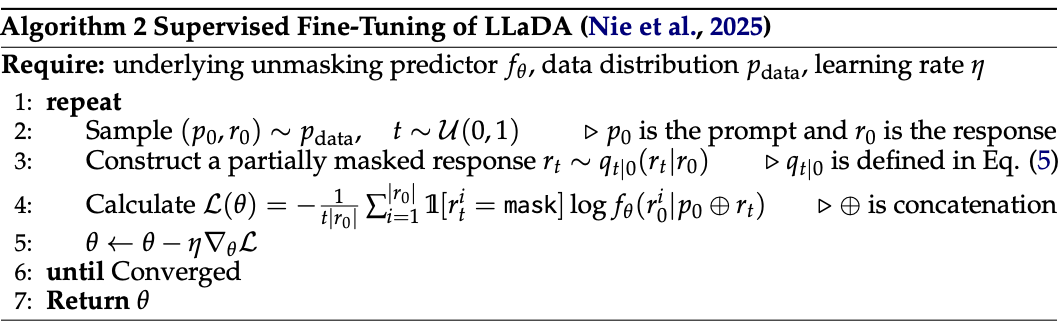
We perform SFT on s1k, a curated dataset consisting of 1000 high-quality reasoning questions. The reasoning traces exhibit detailed step-by-step problem-solving processes, including verification of intermediate results and backtracking when encountering errors.
Stage 2: Efficient Policy Gradient Algorithm for dLLMs - diffu-GRPO
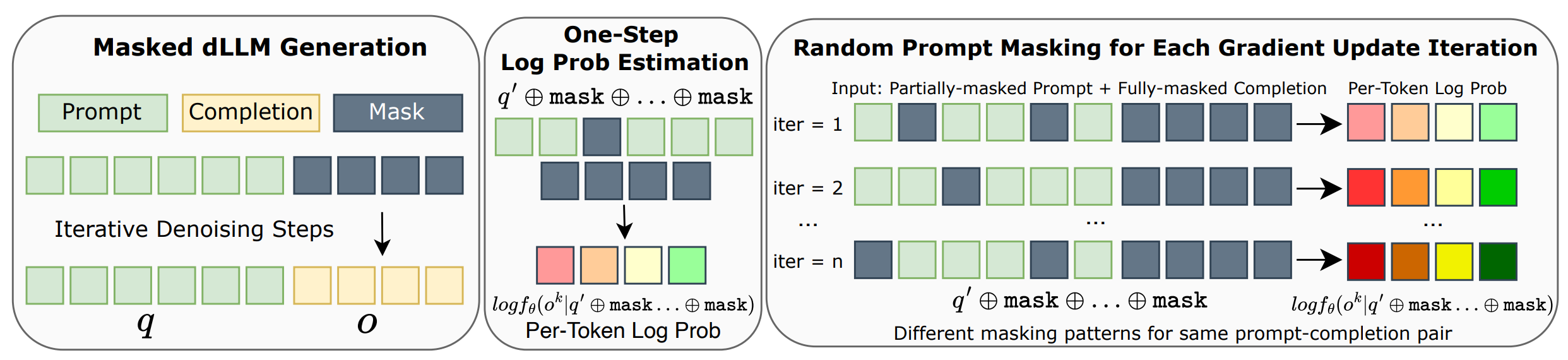
Estimating log-probabilities in dLLMs requires innovative approaches since they lack the natural sequential factorization of autoregressive models.
Adapting RL algorithms to masked dLLMs poses unique challenges since existing approaches for AR models (PPO and GRPO) rely on computing log-probabilities of generated sequences, which cannot be directly applied to dLLMs. While AR models use sequential factorization, dLLMs lack this natural decomposition due to their iterative, non-sequential generation process.
To address this, we propose an efficient log-probability estimator using Mean-Field Approximation of Sequence Log Probability. This approach decomposes sequence-level log-probability with a simple mean-field decomposition and employs One-Step Per-Token Log Probability Estimation with Prompt Masking.
Using this estimator, we extend GRPO to masked dLLMs with the following objective:
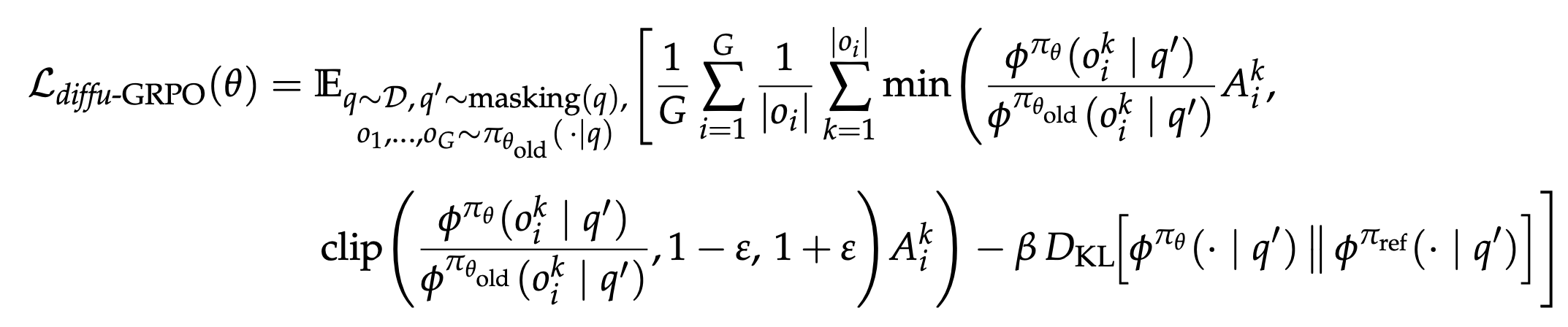
The diffu-GRPO objective builds on GRPO while leveraging our efficient log-probability estimators.
On-policy RL algorithms typically perform multiple gradient updates per batch of samples, requiring a careful balance between outer batch iterations and inner gradient updates. Our log-probability estimator introduces stochastic masking that creates perturbed views of the same (prompt, completion) pairs, serving as regularization for policy optimization. This unique approach allows us to scale the number of inner updates (μ) to higher values while maintaining stable learning dynamics, reducing the number of outer batch iterations and online generations needed—ultimately lowering computational cost significantly.
