Safeguarding the Astronomical Sky (IT)
paper_I_arXiv – paper_II_(arXiv) -> the FULL paper <- press EN_PDF – press IT_PDF
THIS APPEAL HAS BEEN SIGNED BY
2107+ ASTRONOMERS
(the refresh rate of the counter may slow down).
To sign/subscribe follow this link.
This is an international appeal by professional astronomers open for subscription to ask for an intervention from institutions and governments.
Astronomical observations from the ground can be greatly harmed by the ongoing deployment of large satellite fleets in preparation for the next generation of telecommunications.
For centuries the astronomical observations from the ground have led to exceptional progress in our scientific understanding of the Laws of Nature. Currently, the capability of astronomical instrumentation from the ground is endangered by the deployment of satellites fleets.
Through this international appeal and following the same concerns expressed by the International Astronomical Union, IAU [1] and other institutions, we raise a formal request for greater effective protection and safeguard for professional astronomical observations from the ground, guaranteeing the right to observe a sky free from unnecessary artificial polluting sources.
In particular, all the signers, astronomers and collaborators wish to manifest humanly and personally their worry and contrariety to the sky coverage produced by artificial satellites, which represent a dramatic degradation of the scientific content for a huge set of astronomical observations.
The sky degradation is not only due to light pollution in the sky near cities and the most populated areas, but it is also due to artificial satellite fleets crossing and scarring observations with bright parallel streaks/trails at all latitudes.
Astronomers are extremely concerned by the possibility that Earth may be blanketed by tens of thousands of satellites, which will greatly outnumber the approximately 9,000 stars that are visible to the unaided human eye. This is not some distant threat. It’s already happening. The american private company SpaceX has already put 180 of these small satellites, collectively called Starlink, in the sky and plans to constellate the whole sky with about 42,000 satellites (placed at three different quota: 340km, 550km and 1150km). Thus, together with other telecommunication space projects in the near future (i.e. the English OneWeb, the Canadian Telesat, the American Amazon, Lynk and Facebook, the Russian Roscosmos and the Chinese Aerospace Science and Industry corp), there could be over 50,000 small satellites encircling the Earth (at different altitudes) for various telecommunication purposes but mainly delivering internet.
These new satellites are small, mass-produced, and orbit very close to the Earth with the intent to provide speedy internet connection with low-latency signals. But that closeness (~340Km) also makes them more visible, and brighter in the night sky especially when lighted by the Sun (satellites launched by SpaceX, 180 at the present day, are brighter than 99 percent of the population of objects visible by the Earth orbit ).
The current total number of cataloged objects in Earth orbit is less than 20,000 among spacecrafts, rocket bodies, fragmented mission and other related debrids, so with only the nominal Starlink fleet the total number of orbiting objects will triple (see pictures).(*)


In the mid and long term, this will severely diminish our view of the Universe, create more space debris, and, deprive humanity of an unblemished view of the night sky. It has been computed that most of these satellites will be visible to the naked eye (with a brightness between the 3rd and 7th magnitude particularly in the time after sunset and before sunrise, reaching the brightness of the stars in the Ursa Minor constellation (e.g. there are only 172 stars in the whole sky exceeding the expected brightness of Starlink satellites). Thus with 50k satellites the “normality” will be a sky crowded with artificial objects (every one square degree of the sky will have a satellite crawling in it along the whole observing night).
Not only observations with wide-field survey telescopes will be damaged (e.g. LSST [2] capable to scan and perform a survey of the entire sky in three nights or VST [3] with its 268MegaPixels camera and a FOV of 1 square degree or Pan-STARRS [4] with its FOV of 7 square degrees and 1.4 Giga pixels camera, …), but also deep/long exposures with small-field facilities will be unavoidably impaired, see picture and [7].
Considering that large area astronomical observations and sky survey are commonly used in NEO and asteroids monitoring and research related projects to guard the Earth planet from potential impact events, such satellite constellations could negatively impact on the ability to prevent and warn the whole humankind.(*)
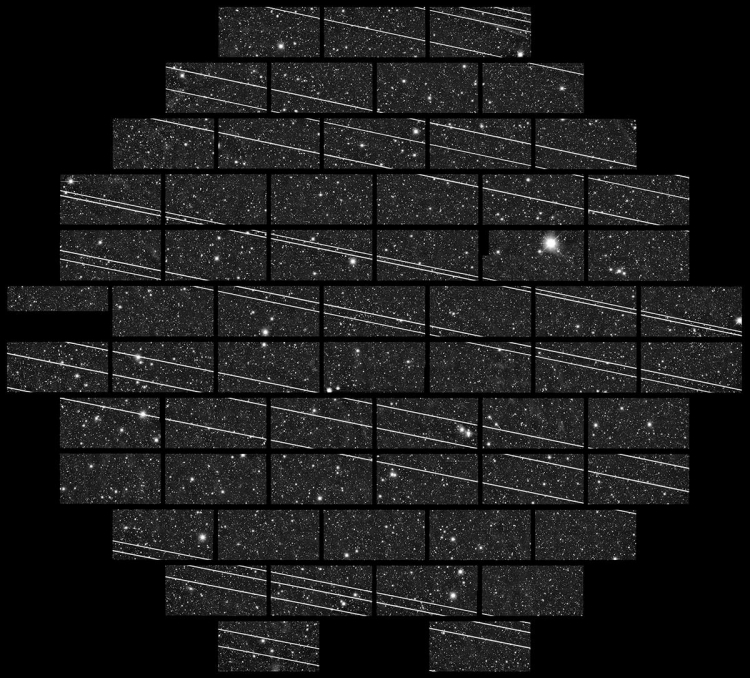
This light pollution is extremely damaging for astronomical observations at all wavelengths. The recent attempt to use non-reflecting paint on the body (i.e. not the solar panels which represents 75% of the reflecting surface) of one of the Starlink satellite (n.1130 DARKSAT), see [8], even if their brightness would reduce to zero (which is impossible since the solar panels, which represent 3/4 of the reflective surface, would remain uncovered), the degradation for scientific observations will remain high for two reasons: 1) the stars and other objects in the universe will be eclipsed, therefore harming time-dependent (variability) studies, and, 2) the reflectivity of surface depends on the observational wavelength, so what becomes dark in one part of the spectrum (e.g. visible) remains bright or shines in other parts of the spectrum (e.g. infrared or radio).(**)
It should also be noted that during nominal service operations SpaceX expects to dismiss and replace from 2,000 to 8,000 Starlink satellites every year, disintegrating them in the lower atmosphere, with all related issues.(*)
What is not widely acknowledged is that the development of the latest generation telecommunication networks (both from space and from Earth) already has a profound impact on radio-astronomical observations (at all sub-bands): with LEO satellite fleets it is feared that the situation will become unbearable.
In particular, low Earth orbit satellite’s spectral windows identified to communicate with earth stations in the Ku (12-18GHz), Ka (27-40GHz) and V (40-75GHz) bands will overlap with the nominal radio-astronomy bands and so will interfere with ground radio telescopes and radio interferometers, making the radio detectors enter in a non-linear regime in the K band (18.26.5GHz) and in Q band (33-50GHz). This fact will irreparably compromise the whole chain of analysis in those bands with repercussions on our understanding of the Universe, or even, making the astrophysics community blind to these spectral windows.
To aggravate the matter, with the current technological development, the planned density of radio frequency transmitters is impossible to envisage. In addition to millions of new commercial wireless hot spot base stations on Earth directly connected to the ~50,000 new satellites in space, will produce at least 200 billion of new transmitting objects, according to estimates, as part of the Internet of Things (IoT) by 2020-2022, and one trillion of objects a few years later. Such a large number of radio-emitting objects could make radio astronomy from ground stations impossible without a real protection made by countries’ safe zones where radio astronomy facility are placed. We wish to avoid that technological development without serious control would turn radio astronomy practice into an ancient extinct science.
FOR ALL THESE REASONS
We, astronomers subscribing to this appeal state THERE IS NO MORE TIME TO DISCUSS, IT IS TIME TO ACT!
ASK GOVERNMENTS, INSTITUTIONS AND AGENCIES ALL AROUND THE WORLD
- to be committed to provide legal protection to ground astronomical facilities in all of the available observation electromagnetic windows.
- to put on hold further Starlink launches (and other projects) and carry out an accurate moratorium on all technologies that can negatively impact astronomical observations from space and from the ground, or impact on the scientific, technological and economic investments that each State engages in astrophysical projects.
- to put in place a clear evaluation of risks and predictive impacts on astronomical observatories (i.e. loss of scientific and economic value), giving stringent guidelines to private individuals, societies and industries to plan satellite investments without clearly understanding all of the negative effects on outstanding astronomical facilities.
- that the US Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and any other national agency be wary of granting permission to ship non-geostationary low-orbit satellites into orbit or alternatively to limit the authorization of only satellites being above the airspace of the “home country”.
- to demand a worldwide orchestration, where national and international astronomical agencies can impose the right of veto on all those projects that negatively interfere with astronomical outstanding facilities.
- to limit and regulate the number of telecommunication satellite fleets to the “strictly necessary number” and to put them in orbit only when old-outdated technology satellites are deorbited, according to the Outer Space Treaty (1967) – the Art IX [5], and the United Nations Guidelines for the Long-term Sustainability of Outer Space Activities (2018) – guideline 2.2(c) [6], requiring the use of outer space be conducted “so as to avoid [its] harmful contamination and also adverse changes in the environment of the Earth” and […omissis…] risks to people, property, public health and the environment associated with the launch, in-orbit operation and re-entry of space objects”.
FINALLY
All of these requests come from the heartfelt concern of scientists arising from threatens to be barred from accessing the full knowledge of the Cosmos and the loss of an intangible asset of immeasurable value for humanity. In this context, all co-signers of this appeal consider ABSOLUTELY NECESSARY to put in place all possible measures to protect the night sky right also on the legal side. It would be desirable to adopt contingent and limiting resolutions to be ratified with shared international rules, which must be adopted by all space agencies to ensure protection for astronomical bands observable from the ground. All of this to continue to admire and study our Universe, for as long as possible.
References:
[1] https://www.iau.org/ – https://www.iau.org/news/announcements/detail/ann19035/?lang
[2] https://www.lsst.org – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vera_C._Rubin_Observatory
[3] https://www.eso.org/public/ – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VLT_Survey_Telescope
[4] https://panstarrs.stsci.edu/
[5] https://www.unoosa.org/oosa/en/ourwork/spacelaw/treaties/introouterspacetreaty.html
[7] Simulated prediction of “only” 12k Starlink satellites in the sky: https://youtu.be/LGBuk2BTvJE and https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z9hQfKd9kfA
[8] Visualization tool to find, plot and search satellite orbits: https://celestrak.com/cesium/orbit-viz.php?tle=/satcat/tle.php?INTDES=2020%2D001&satcat=/pub/satcat.txt&orbits=20&pixelSize=3&samplesPerPeriod=90
This appeal/petition can be signed by professional Astrophysicists & Astronomers, Technologists/Engineers , Collaborators & PHD Students involved in professional astronomical observations.
Note that (*) Such a sentence was added the 13/01/2020.
Note that (**) Such a sentence was added the 16/01/2020.











