- Popular Comparisons
- FrontRunners
- Buyers Guide
- Related Software
Compare Products
Showing 1 - 25 of 641 products


NetSuite is an AI-powered cloud-based business management suite that incorporates ERP, financial management, CRM and eCommerce f...Read more about NetSuite
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Salesforce Sales Cloud
NetSuite's Best Rated Features
NetSuite's Worst Rated Features


Funnel is the leading marketing data hub designed to help marketing teams own their performance. With Funnel, marketers connec...Read more about Funnel
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Google Analytics 360


Organizations face increasing demands for high-powered analytics that produce fast, trustworthy results. Whether it’s providing ...Read more about SAS Viya
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Google Drive
SAS Viya's Best Rated Features
SAS Viya's Worst Rated Features


Pliable is a data organization platform designed to structure and connect business data, making it clean, reliable, and ready fo...Read more about Pliable
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
PayPal


Grow is a cloud-based, business analytics and reporting solution suitable for small to midsize organizations. The solution allow...Read more about Grow
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Google Drive
Grow's Best Rated Features
4.75Customizable Dashboard
See All
Grow's Worst Rated Features


Phocas is a SaaS platform designed to help mid-market businesses in manufacturing, wholesale distribution, and retail make data-...Read more about Phocas
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Microsoft Excel
Phocas's Best Rated Features
4.89Scheduled/Automated Reports
See All
Phocas's Worst Rated Features


Logi Symphony solves business intelligence's core problem: users shouldn't leave their workflow for insights. Our platform embed...Read more about Logi Symphony
Logi Symphony's Best Rated Features
Logi Symphony's Worst Rated Features

Amazon QuickSight's Best Rated Features
4.57Self Service Data Preparation
See All
Amazon QuickSight's Worst Rated Features


Better Reports is a web-based SaaS tool that provides powerful analytics for popular apps. Businesses can get instant access to...Read more about Better Reports
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Shopify
Better Reports's Best Rated Features
Better Reports's Worst Rated Features


ImportYeti is a US Bill of Lading data platform that offers information on suppliers of any US company. The platform retrieves d...Read more about ImportYeti
ImportYeti's Best Rated Features
ImportYeti's Worst Rated Features


Custom Platform to increase Adoption, Conversion and Retention, at a fraction of the cost. Germain UX helps Monitor, Analyze, I...Read more about Germain UX
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
WordPress


In the dynamic landscape of e-commerce, stay steps ahead with Prisync's advanced competitor price tracking software. Eliminate t...Read more about Prisync
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Shopify
Prisync's Best Rated Features
4.89Competitor Price Tracking
See All
Prisync's Worst Rated Features


Are you spending your marketing budget effectively? Which products or channels bring in the best long-term customers? What are c...Read more about Lebesgue
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Shopify
Lebesgue's Best Rated Features
Lebesgue's Worst Rated Features


Dreamdata is a B2B Activation & Attribution Platform that provides the most complete B2B customer journey map anywhere. This em...Read more about Dreamdata
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
HubSpot CRM
Dreamdata's Best Rated Features
5.0Multi-Channel Attribution
See All
Dreamdata's Worst Rated Features


Entrinsik Informer is a business intelligence tool that is designed for business and IT professionals. Key features include a da...Read more about Informer
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Box


Google Cloud is a suite of cloud computing services that allows businesses to build, deploy, and scale applications. The platfor...Read more about Google Cloud
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Google Docs
Google Cloud's Best Rated Features
Google Cloud's Worst Rated Features
3.91Role-Based Permissions
See All


Rayven designs and delivers operational systems for industrial and asset-intensive businesses. Most operations run on a mix of ...Read more about Rayven
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Google Drive
Rayven's Best Rated Features
Rayven's Worst Rated Features


Upgrade to Reach Reporting. AI-Enhanced Financial Reporting Automated reports, deep analysis, and visualized data in seconds, ...Read more about Reach Reporting
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
QuickBooks Online
Reach Reporting's Best Rated Features
Reach Reporting's Worst Rated Features


SmartPM is an AI-driven Automated Project Controls™ and Schedule Analytics solution built for construction. From handling intr...Read more about SmartPM
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Procore
SmartPM's Best Rated Features
SmartPM's Worst Rated Features


Competitors App is a business intelligence tool that allows users to monitor and analyze competitors' marketing strategies. The ...Read more about Competitors App
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Slack


Alteryx Designer is a desktop-based self-service data profiling, preparation, blending, and analytics product used to create vis...Read more about Alteryx Designer
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Tableau
Alteryx Designer's Best Rated Features
Alteryx Designer's Worst Rated Features


The AI era demands unprecedented adaptability. Traditional software and rigid legacy systems that were designed for static tasks...Read more about MongoDB
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Microsoft Excel
MongoDB's Best Rated Features
4.68Multiple Programming Languages Supported
See All
MongoDB's Worst Rated Features


800response is a lead generation solution that helps businesses of all sizes streamline operations across call monitoring, routi...Read more about 800response
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Microsoft Excel
800response's Best Rated Features
800response's Worst Rated Features


Effortlessly create and display real-time TV dashboards with Geckoboard. Tailored for busy team leads and managers, Geckoboard...Read more about Geckoboard
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
PayPal
Geckoboard's Best Rated Features
Geckoboard's Worst Rated Features


At Similarweb, we help businesses make smarter decisions in the digital age. Whether it’s understanding your competitors or unco...Read more about Similarweb
Integrations
Integrations
![]()
Salesforce Sales Cloud
Similarweb's Best Rated Features
Similarweb's Worst Rated Features
3.33Social Media Monitoring
See All
1
2345...
26Buyers Guide
This detailed guide will help you find and buy the right business intelligence software for you and your business.
Last Updated on January 27, 2025Business intelligence (BI) software has gained considerable traction since its introduction as "decision support systems" in the 1960s. Today, there are over 100 BI software companies selling business intelligence tools.
We put together this buyer's guide to help buyers understand the BI tools market. In this guide, we'll review:
What is business intelligence software?
Comparing business intelligence tools
Common Features of Business Intelligence Software
What is business intelligence software?
Business intelligence software is data visualization and data analytics software that helps organizations make more well-informed decisions. Business intelligence tools connect to the business's data warehouse, ERP systems, marketing data, social media channels, Excel data imports, or even macroeconomic information.
The business intelligence market is growing rapidly because of the proliferation of data to analyze. Over the past few decades, companies that have deployed Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and other applications are now sitting on a mountain of data that can be analyzed. In addition, the growth of the Web has increased the demand for data analysis tools that can analyze large data sets.
One of the biggest trends in the BI market is the shift in software architecture and design to more user-friendly self-service applications. These applications are now being used by business users—not just IT staff—to pull ad-hoc reports, create interactive dashboards, and even allow end users to perform advanced analytics functions on the BI platform.
Medical practices and doctors looking for solutions that can function with their existing medical software might be interested in healthcare BI software.
There are many popular BI solutions on the market, and it can be hard to know what distinguishes one product from another and which is right for you. To help you better understand how the top BI systems stack up against one another, we created a series of side-by-side product comparison pages that break down the details of what each solution offers in terms of pricing, applications, ease of use, support and more:
Top Qlik Sense Comparisons | Top Qlikview Comparisons | Top Tableau Comparisons |
Qlik Sense vs. Qlikview Qlik Sense vs. Tableau | Qlik Sense vs. Qlikview Qlikview vs. Spotfire | Qlik Sense vs. Tableau Spotfire vs. Tableau |
Top Spotfire Comparisons | ||
Qlikview vs. Spotfire Spotfire vs. Tableau |
Common Features of Business Intelligence Software
BI software can be divided into three broad application categories: data management tools, data discovery applications and reporting tools (including interactive dashboards and data visualization software). In the next section, we'll explain how these analytics platforms can help your organization's decision-making process become more data-driven.
The BI tool you'll need depends on how your data is currently managed and how you would like to analyze it. For example, if it is currently scattered across disparate transactional databases, you might need to build a data warehouse to centralize it and invest in data management tools that offer Extract, Transform and Load (ETL) functionality to move and re-structure it.
Once data is given a common structure and format, you can invest in data discovery solutions such as Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), data mining and semantic or text mining applications, with the capability to create custom, ad hoc reports. And because information is stored within the warehouse, users can quickly pull reports without impacting the performance of the organization’s software applications, such as CRM, ERP and supply chain management solutions.
We’ve illustrated this concept in the image below:
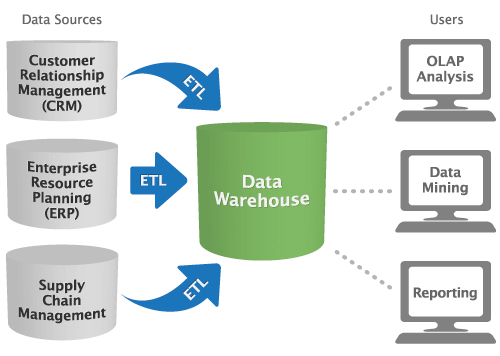
But this isn’t the only way to implement business intelligence software within your organization. If you’re only analyzing data from a single source, ETL and data warehouses are unnecessary. Alternatively, you might require multiple warehouses, and thus, require different tools to connect data between both these servers and other analytics tools that need access to this data.
Regardless of your unique business needs, any BI tool you buy should have some key features:
Data quality management
Extract, transform and load (ETL)
Data mining
Online analytical processing (OLAP)
Predictive analytics
Semantic and text analytics
Data visualizations
Interactive dashboards
Report writers
Scorecarding
Ad hoc reporting
Better decision-making starts with better data. Data management tools help clean up "dirty data," organize information by providing format and structure and prepare data sources for analyses.
Functionality | Description |
Data quality management | Helps organizations maintain clean, standardized and error-free data. Standardization is especially important for business intelligence tools that integrate data from diverse sources. Data quality management ensures that later analyses are correct and can lead to improvements within the business. |
Extract, transform and load (ETL) | Collects data from outside sources, transforms it and then loads it into the target system (a database or a data warehouse). Because primary data is often organized using different schemas or formats, analysts can use ETL tools to normalize it for use in analytics. |
Data discovery applications
The ability to sift through data and come to meaningful conclusions is one of the most powerful benefits of adopting business intelligence tools. Data discovery applications help users make sense of their data, whether it be through quick, multivariate analysis during OLAP or via advanced algorithms and statistical computations during data mining.
Functionality | Description |
Sorts through large amounts of data to identify new or unknown patterns. It is often the first step that other processes rely on, such as predictive analytics. Databases are often too large or convoluted to find patterns with the naked eye or through simple queries. Data mining helps point users in the right direction for further analysis by providing an automated method of discovering previously neglected trends. | |
Online analytical processing (OLAP) | Enables users to quickly analyze multidimensional data from different perspectives. It is typically made up of three analytical operations: data consolidation, data sorting and classification ("drill-down"), and data analytics from a particular perspective ("slice-and-dice"). For example, a user could analyze sales numbers for various products by store and by month. OLAP allows users to produce this analysis. |
Analyzes current and historical data to make predictions about future risks and opportunities. An example of this is credit scoring, which relies on an individual's current financial standing to make predictions about their future credit behavior. | |
Semantic and text analytics | Extracts and interprets large volumes of text to identify patterns, relationships and sentiment. For example, the popularity of social media has made text analytics valuable to companies with a large social footprint. Understanding semantic trends is a powerful tool for organizations evaluating purchase intent or customer satisfaction among users of these channels. |
In the words of John W. Tuckey, “the greatest value of a picture is when it forces us to notice what we never expected to see.” Reporting applications are an important way to present data and easily convey the results of analysis.
Business intelligence users are increasingly business users—not IT staff—who need quick, easy-to-understand displays of information. In response, software vendors have been working to mask the complexity of these applications and increasingly focus on the user experience.
Functionality | Description |
Helps users create advanced interactive dashboard representations of data via simple user interfaces. The ability to visualize information in a graphical format (as opposed to words or numbers) can help users understand data in a more insightful way. In addition, new interactive tools can help teams use analytics and manipulate reports in real-time. | |
Dashboards typically highlight key performance indicators (KPIs), which help managers focus on the metrics that are most important to them. Dashboards are often browser-based, making them easily accessible by anyone with permissions. | |
Report writers | Allows users to design and generate custom reports. Many CRM and ERP systems include built-in BI reporting tools, but users can also purchase standalone applications, such as Crystal Reports, to create ad hoc reports based on complex queries. This is especially helpful for organizations that constantly use analytics and need to generate new reports quickly. |
Scorecarding | Scorecards attach a numerical weight to performance and map progress toward goals. Think of it as dashboards taken one step further. In organizations with a strategic performance-management methodology (e.g., balanced scorecard, Six Sigma etc.), scorecards are an effective way to keep tabs on key metrics. For example, a scorecard might establish a grade of “A+" to 40 percent year-over-year growth if the goal was set at 14 percent. |
What type of buyer are you?
Before evaluating software, you must determine what type of buyer you are.
Business users and departmental buyers. These buyers favor small data-discovery vendors and BI tools over the big, traditional BI systems. Ease-of-use and fast deployment are more important than in-depth functionality and integration. They are usually business users rather than IT staff.
IT buyers. Traditional buyers are more focused on functionality and integration within their information infrastructure stacks or other ERP applications. Integration across different entities and departments is usually more important than ease of use.
Market trends to understand
As you begin your software comparison and evaluation, there are a couple trends to consider:
In-memory processing: OLAP systems of the past would pre-calculate every possible combination of data. These calculations would be stored in the “cube,” and users could retrieve them when they needed a certain analysis. Creating these cubes was very time-consuming—sometimes taking as long as a year—and required expertise. Today, computer processors and memory are faster, cheaper and more powerful overall. This same process can happen in-memory, rather than using a disk-based approach with cubes. Analytics software built on an in-memory architecture can retrieve data and perform calculations in real-time or on-the-fly.
Big Data: The Internet is rapidly creating vast amounts of data. This phenomenon is known as "big data" among IT and business leaders. Business analytics software companies are beefing up their data warehousing and analytics capabilities to keep up with demand.
However, according to Gartner, through 2015, 85% of Fortune 500 organizations will be unable to exploit big data for competitive advantage. The right BI tools can help harness the power of so much data.
Companies dealing with large amounts of data may also want to consider investing in dedicated IT security suites to support their computer security needs.
Business users to outnumber IT staff: This is a major trend playing out in the market. More business users—rather than traditional IT staff—are evaluating and purchasing software. So usability is becoming more important than functionality during software evaluations. As a result, small data discovery vendors that develop really good interactive visualization tools are gaining market share. Meanwhile, traditional BI vendors are parroting new market entrants by promoting ease of use.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): A growing number of organizations are considering SaaS or “cloud” BI software instead of traditional, on-premise software that you install on-location. Cost is a major driver of this trend. The poorly performing economy is motivating companies to look at lower-cost BI software from SaaS and open source vendors. Of course, perceived ease of use, faster implementations and reduced IT needs are also driving this trend. On-premise BI vendors are responding by committing development resources to cloud technology.
**[
Mobile BI applications:]()** Proliferation of the iPhone, iPad and other mobile devices is pushing vendors (e.g., Microsoft and Oracle) to develop on-the-go business intelligence applications. Analysts think mobile BI could expand the population of BI users to a larger, mainstream audience.